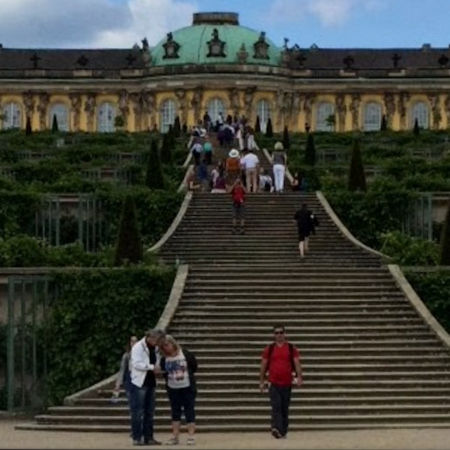
Sanssouci, Potsdam. Sanssouci was the summer palace of Frederick the Great, King of Prussia, in Potsdam, near Berlin. It is often counted among the German rivals of Versailles. While Sanssouci is in the more intimate Rococo style and is far smaller than its French Baroque counterpart, it too is notable for the numerous temples and follies in the park. The palace was designed/built by Georg Wenzeslaus von Knobelsdorff between 1745 and 1747 to fulfill King Frederick's need for a private residence where he could relax away from the pomp and ceremony of the Berlin court. The palace's name emphasises this; it is a French phrase, which translates as without concerns, meaning without worries or carefree, symbolising that the palace was a place for relaxation rather than a seat of power. The name in past times reflected a play on words, with the insertion of a comma visible between the words Sans and Souci, viz. Sans, Souci. Kittsteiner theorizes that this could be a philosophical play on words, meaning without a worry/concern or it could be some secret personal message which nobody has interpreted, left to posterity by Frederick II. Sanssouci is little more than a large, single-story villa, more like the Chateau de Marly than Versailles. Containing just ten principal rooms, it was built on the brow of a terraced hill at the centre of the park. The influence of King Frederick's personal taste in the design and decoration of the palace was so great that its style is characterised as Frederician Rococo, and his feelings for the palace were so strong that he conceived it as a place that would die with him. Because of a disagreement about the site of the palace in the park, Knobelsdorff was fired in 1746. Jan Bouman, a Dutch architect, finished the project. During the 19th century, the palace became a residence of Frederick William IV. He employed the architect Ludwig Persius to restore and enlarge the palace, while Ferdinand von Arnim was charged with improving the grounds and thus the view from the palace. The town of Potsdam, with its palaces, was a favourite place of residence for the German imperial family until the fall of the Hohenzollern dynasty in 1918. After World War II, the palace became a tourist attraction in East Germany. Following German reunification in 1990, Frederick's body was returned to the palace and buried in a new tomb overlooking the gardens he had created. Sanssouci and its extensive gardens became a World Heritage Site in 1990 under the protection of UNESCO; in 1995, the Prussian Palaces and Gardens Foundation Berlin-Brandenburg was established to care for Sanssouci and the other former imperial palaces in and around Berlin. These palaces are now visited by more than two million people a year from all over the world. The location and layout of Sanssouci above a vineyard reflected the pre-Romantic ideal of harmony between man and nature, in a landscape ordered by human touch. Winemaking, however, was to take second place to the design of the palace and pleasure gardens. The hill on which Frederick created his terrace vineyard was to become the focal point of his demesne, crowned by the new, but small, palace, mein Weinbergheuschen, as Frederick called it. With its extensive views of the countryside in the midst of nature, Frederick wanted to reside there sans souci and to follow his personal and artistic interests. Hence, the palace was intended for the use of Frederick and his private guests, his sketch indicated the balanced suites pour les etrangers and pour le roy, only during the summer months, from the end of April to the beginning of October. Twenty years following his creation of Sanssouci, Frederick built the New Palace in the western part of the park. This far larger palace was in direct contrast to the relaxed ethos behind Sanssouci, and displayed Frederick's power and strength to the world, in the Baroque style. The design of the New Palace was intended to demonstrate that Prussia's capabilities were undiminished despite its near defeat in the Seven Years' War. Frederick made no secret of his intention, even referring to the new construction as his fanfaronnade. This concept of a grand palace designed to impress has led to the comparison of the palaces of Potsdam to Versailles, with Sanssouci being thrust into the role of one of the Trianons. This analogy, though easy to understand, ignores the original merits of the concept behind Sanssouci, the palace for which the whole park and setting were created.
more...