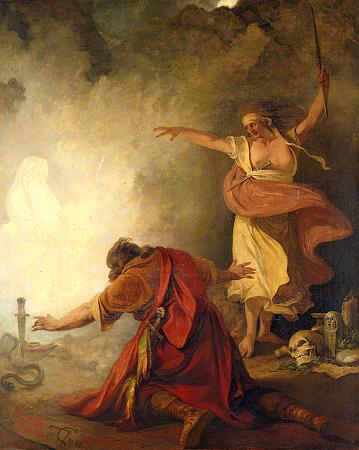
Saul. Saul, according to the Hebrew Bible, was the first king of the Kingdom of Israel and Judah.
His reign, traditionally placed in the late 11th century BCE, supposedly marked a transition from a tribal society to statehood. Saul's life and reign are described in the Hebrew Bible.
He was anointed by the prophet Samuel and reigned from Gibeah. He fell on his sword to avoid capture in the battle against the Philistines at Mount Gilboa, during which three of his sons were also killed.
The succession to his throne was contested by Ish-bosheth, his only surviving son, and his son-in-law David, who eventually prevailed. According to the Hebrew text of the Bible Saul was thirty years old when he came to the throne and reigned for forty years, but scholars generally agree that the text is faulty and that a reign of twenty or twenty-two years is more probable.
The biblical accounts of Saul's life are found in the Books of Samuel: According to the Tanakh, Saul was the son of Kish, of the family of the Matrites, and a member of the tribe of Benjamin, one of the twelve Tribes of Israel. It appears that he came from Gibeah. Saul married Ahinoam, daughter of Ahimaaz, with whom he sired four sons and two daughters. Saul also had a concubine named Rizpah, daughter of Aiah, who bore him two sons, Armoni and Mephibosheth. Saul died at the Battle of Mount Gilboa, and was buried in Zelah, in the regio
His reign, traditionally placed in the late 11th century BCE, supposedly marked a transition from a tribal society to statehood. Saul's life and reign are described in the Hebrew Bible.
He was anointed by the prophet Samuel and reigned from Gibeah. He fell on his sword to avoid capture in the battle against the Philistines at Mount Gilboa, during which three of his sons were also killed.
The succession to his throne was contested by Ish-bosheth, his only surviving son, and his son-in-law David, who eventually prevailed. According to the Hebrew text of the Bible Saul was thirty years old when he came to the throne and reigned for forty years, but scholars generally agree that the text is faulty and that a reign of twenty or twenty-two years is more probable.
The biblical accounts of Saul's life are found in the Books of Samuel: According to the Tanakh, Saul was the son of Kish, of the family of the Matrites, and a member of the tribe of Benjamin, one of the twelve Tribes of Israel. It appears that he came from Gibeah. Saul married Ahinoam, daughter of Ahimaaz, with whom he sired four sons and two daughters. Saul also had a concubine named Rizpah, daughter of Aiah, who bore him two sons, Armoni and Mephibosheth. Saul died at the Battle of Mount Gilboa, and was buried in Zelah, in the regio
Wikipedia ...