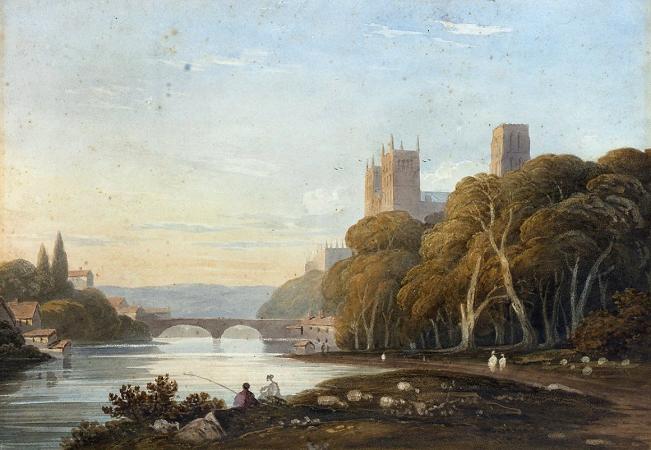
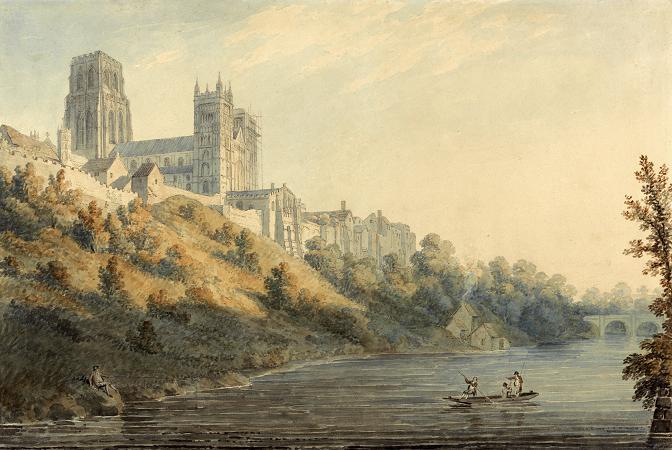Durham Cathedral. The Cathedral Church of Christ, Blessed Mary the Virgin and St Cuthbert of Durham, commonly known as Durham Cathedral and home of the Shrine of St Cuthbert, is a cathedral in the city of Durham, England. It is the seat of the Bishop of Durham, the fourth-ranked bishop in the Church of England hierarchy. The present cathedral was begun in 1093, replacing the Saxon 'White Church', and is regarded as one of the finest examples of Norman architecture in Europe. In 1986 the cathedral and Durham Castle were designated a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Durham Cathedral holds the relics of Saint Cuthbert, transported to Durham by Lindisfarne monks in the ninth century, the head of Saint Oswald of Northumbria, and the remains of the Venerable Bede. In addition, its library contains one of the most complete sets of early printed books in England, the pre-Dissolution monastic accounts, and three copies of Magna Carta. From 1080 until 1836 the Bishop of Durham held the powers of an Earl Palatine, exercising military and civil leadership as well as religious leadership, in order to protect the English Border with Scotland. The cathedral walls formed part of Durham Castle, the chief seat of the Bishop of Durham. There are daily Church of England services at the cathedral, with the Durham Cathedral Choir singing daily except Mondays and when the choir is on holiday. It is a major tourist attraction and received 694,429 visitors in 2018. The See of Durham takes its origins from the Diocese of Lindisfarne, founded by Saint Aidan at the behest of Oswald of Northumbria in about 635, which was translated to York in 664. The see was reinstated at Lindisfarne in 678 by the Archbishop of Canterbury. Among the many saints who originated at Lindisfarne Priory, the greatest was Saint Cuthbert, Bishop of Lindisfarne from 685 until his death in 687, who is central to the development of Durham Cathedral. After repeated Viking raids, the monks fled from Lindisfarne in 875, carrying Saint Cuthbert's relics with them. The diocese of Lindisfarne remained itinerant until 882, when the monks resettled at Chester-le-Street, 60 miles south of Lindisfarne and 6 miles north of Durham. The see remained at Chester-le-Street until 995, when further Viking incursions once again caused the monks to move with their relics. According to the local legend of the Dun Cow and the Saint's hagiography, the monks followed two milk maids who were searching for a dun-coloured cow and found themselves on a peninsula formed by a loop in the River Wear. Thereupon Cuthbert's coffin became immovable, which was taken as a sign that the new shrine should be built on that spot, which became the City of Durham. A more prosaic set of reasons for the selection of the peninsula is its highly defensible position, and that a community established there would enjoy the protection of the Earl of Northumbria, with whom the bishop at this time, Aldhun, had strong family connections. Today the street leading from The Bailey past the Cathedral's eastern towers up to Palace Green is named Dun Cow Lane due to the miniature dun cows which used to graze in the pastures nearby. Initially, a very simple temporary structure was built from local timber to house the relics of Saint Cuthbert. The shrine was then transferred to a sturdier, probably still in wooden, building known as the White Church. This church was itself replaced three years later in 998 by a stone building also known as the White Church, which in 1018 was complete except for its tower. Durham soon became a site of pilgrimage, encouraged by the growing cult of Saint Cuthbert. King Canute was one of the early pilgrims, and granted many privileges and estates to the Durham monks. The defensible position, flow of money from pilgrims and power embodied in the church at Durham all encouraged the formation of a town around the cathedral, which established the core of the city. The present cathedral was designed and built under William de St-Calais who in 1080 was appointed as the first Prince-Bishop by King William the Conqueror. In 1083 he founded the Benedictine Priory of St. Cuthbert at Durham and having ejected the secular canons who had been in charge of the church and shrine of St Cuthbert there, replaced them with monks from the monasteries of Wearmouth and Jarrow. The extensive lands of the church he divided between his own bishopric and the new Priory. He appointed Aldwin as the first prior. Bishop William of St. Calais demolished the old Saxon church, and on 11 August 1093, together with Prior Turgot of Durham, he laid the foundation stone of the great new cathedral.
more...