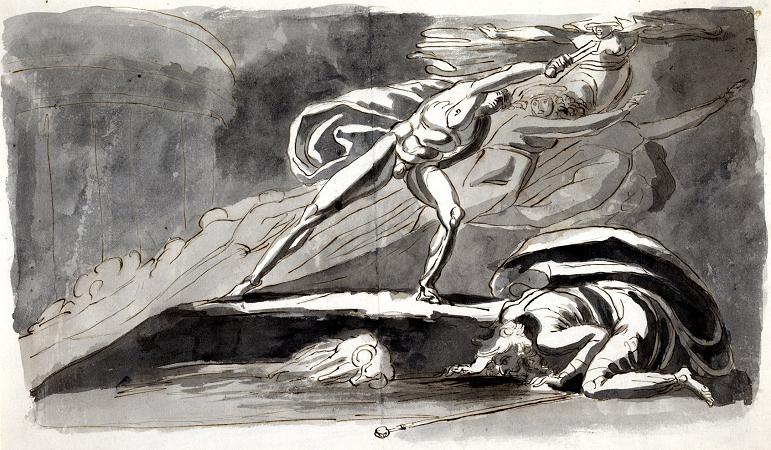
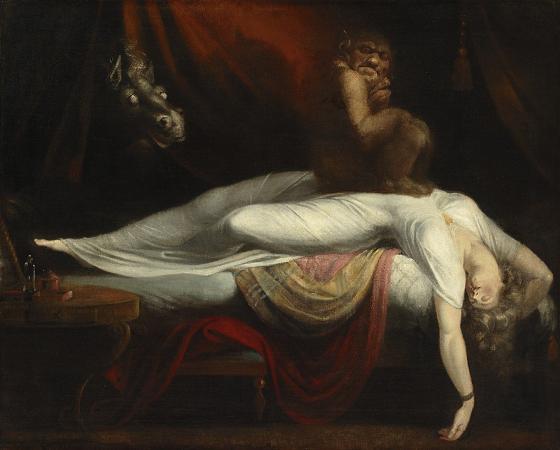
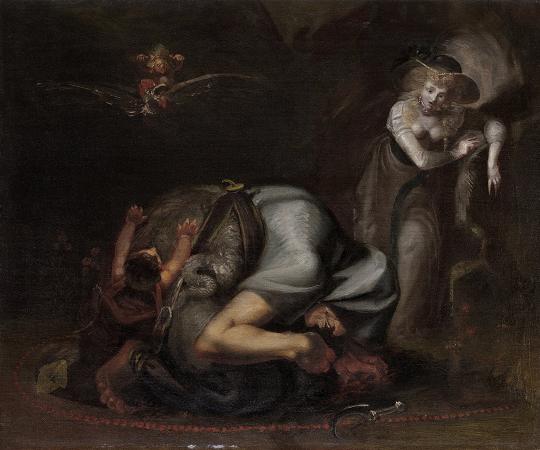
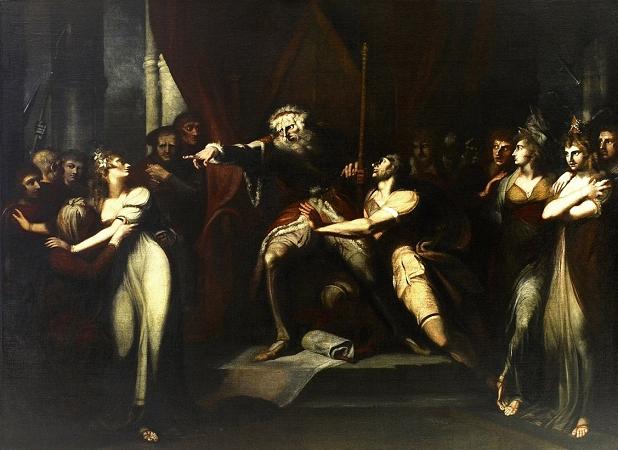
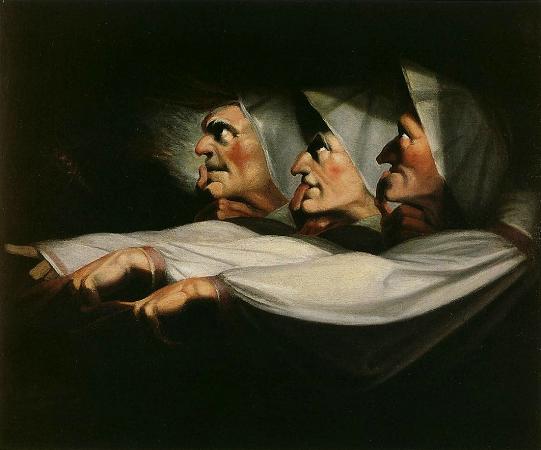
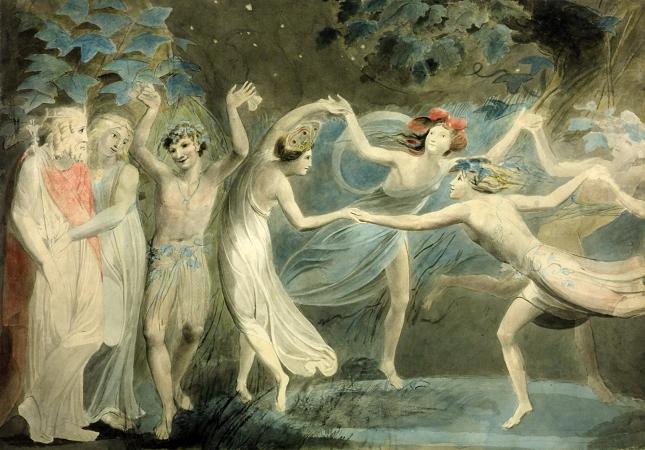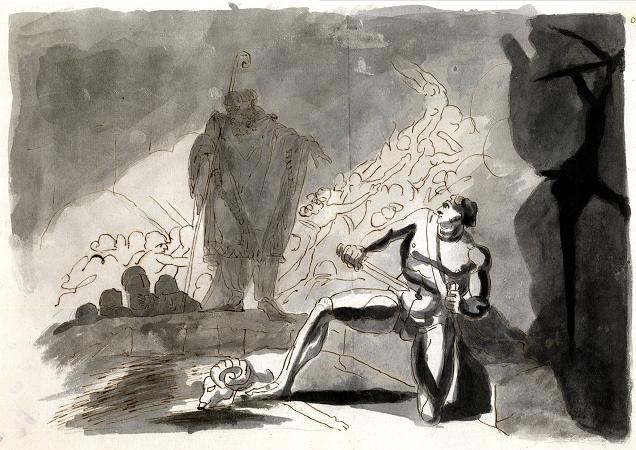Henry Fuseli (1741 - 1825). Henry Fuseli was a Swiss painter, draughtsman and writer on art who spent much of his life in Britain. Many of his works, such as The Nightmare, deal with supernatural subject-matter. He painted works for John Boydell's Shakespeare Gallery, and created his own Milton Gallery. He held the posts of Professor of Painting and Keeper at the Royal Academy. His style had a considerable influence on many younger British artists, including William Blake. Fuseli was born in Zürich, Switzerland, the second of 18 children. His father was Johann Caspar Füssli, a painter of portraits and landscapes, and author of Lives of the Helvetic Painters. He intended Henry for the church, and sent him to the Caroline college of Zurich, where he received an excellent classical education. One of his schoolmates there was Johann Kaspar Lavater, with whom he became close friends. After taking orders in 1761 Fuseli was forced to leave the country as a result of having helped Lavater to expose an unjust magistrate, whose powerful family sought revenge. He travelled through Germany, and then, in 1765, visited England, where he supported himself for some time by miscellaneous writing. Eventually, he became acquainted with Sir Joshua Reynolds, to whom he showed his drawings. Following Reynolds' advice, he decided to devote himself entirely to art. In 1770 he made an art-pilgrimage to Italy, where he remained until 1778, changing his name from Füssli to the more Italian-sounding Fuseli. Early in 1779 he returned to Britain, taking in Zürich on his way. In London he found a commission awaiting him from Alderman Boydell, who was then setting up his Shakespeare Gallery. Fuseli painted a number of pieces for Boydell, and published an English edition of Lavater's work on physiognomy. He also gave William Cowper some valuable assistance in preparing a translation of Homer. In 1788 Fuseli married Sophia Rawlins, and he soon after became an associate of the Royal Academy. The early feminist Mary Wollstonecraft, whose portrait he had painted, planned a trip with him to Paris, and pursued him determinedly, but after Sophia's intervention the Fuselis' door was closed to her forever. Fuseli later said I hate clever women. They are only troublesome. In 1790 he became a full Academician, presenting Thor Battering the Midgard Serpent as his diploma work. In 1799 Fuseli was appointed professor of painting to the Academy. Four years later he was chosen as Keeper, and resigned his professorship, but resumed it in 1810, continuing to hold both offices until his death. As Keeper, he was succeeded by Henry Thomson. In 1799 Fuseli exhibited a series of paintings from subjects furnished by the works of John Milton, with a view to forming a Milton gallery comparable to Boydell's Shakespeare gallery. There were 47 Milton paintings, many of them very large, completed at intervals over nine years. The exhibition proved a commercial failure and closed in 1800. In 1805 he brought out an edition of Pilkington's Lives of the Painters, which did little for his reputation. Antonio Canova, when on his visit to England, was much taken with Fuseli's works, and on returning to Rome in 1817 caused him to be elected a member of the first class in the Academy of St Luke. As a painter, Fuseli favoured the supernatural. He pitched everything on an ideal scale, believing a certain amount of exaggeration necessary in the higher branches of historical painting. In this theory he was confirmed by the study of Michelangelo's works and the marble statues of the Monte Cavallo, which, when at Rome, he liked to contemplate in the evening, relieved against a murky sky or illuminated by lightning. Describing his style, the 1911 edition of the Encyclopædia Britannica said that: His figures are full of life and earnestness, and seem to have an object in view which they follow with intensity. Like Rubens he excelled in the art of setting his figures in motion. Though the lofty and terrible was his proper sphere, Fuseli had a fine perception of the ludicrous. The grotesque humour of his fairy scenes, especially those taken from A Midsummer-Night's Dream, is in its way not less remarkable than the poetic power of his more ambitious works. Though not noted as a colourist, Fuseli was described as a master of light and shadow. Rather than setting out his palette methodically in the manner of most painters, he merely distributed the colours across it randomly. He often used his pigments in the form of a dry powder, which he hastily combined on the end of his brush with oil, or turpentine, or gold size, regardless of the quantity, and depending on accident for the general effect. This recklessness may perhaps be explained by the fact that he did not paint in oil until the age of 25.
more...