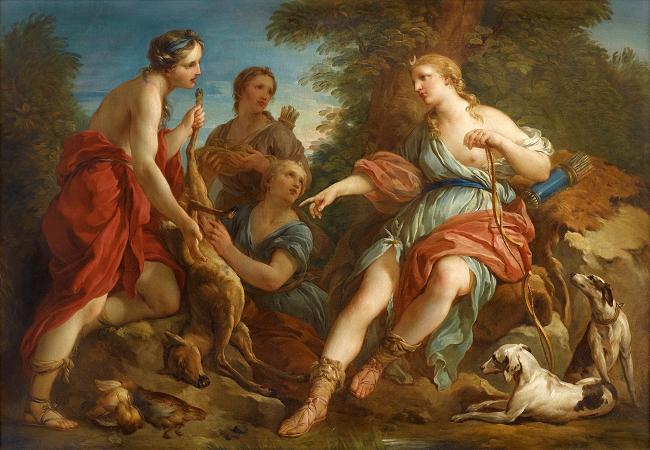
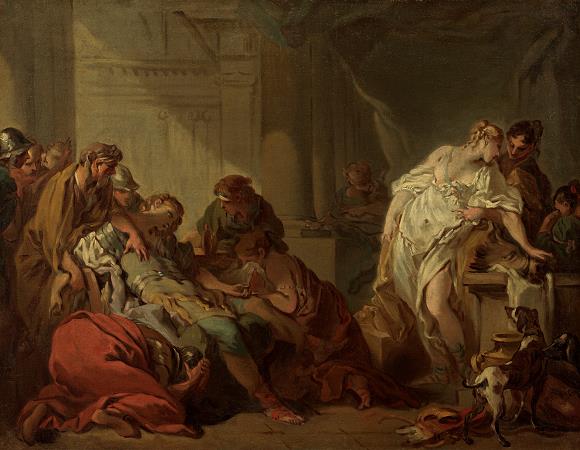
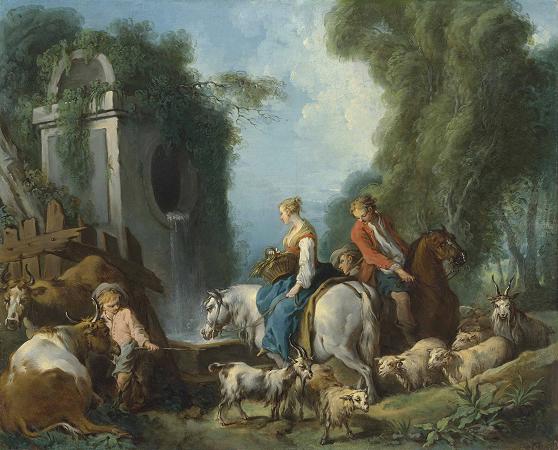
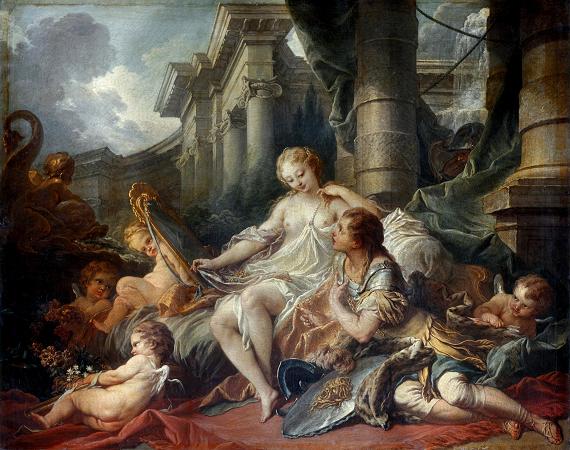
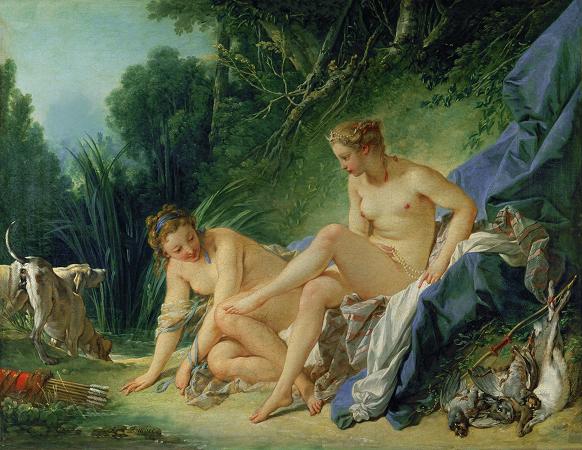
Francois Boucher (1703 - 1770). François Boucher was a French painter, draughtsman and etcher, who worked in the Rococo style. Boucher is known for his idyllic and voluptuous paintings on classical themes, decorative allegories, and pastoral scenes. He was perhaps the most celebrated painter and decorative artist of the 18th century. A native of Paris, Boucher was the son of a lesser known painter Nicolas Boucher, who gave him his first artistic training. At the age of seventeen, a painting by Boucher was admired by the painter François Lemoyne. Lemoyne later appointed Boucher as his apprentice, but after only three months, he went to work for the engraver Jean-François Cars. In 1720, he won the elite Grand Prix de Rome for painting, but did not take up the consequential opportunity to study in Italy until five years later, due to financial problems at the Académie royale de peinture et de sculpture. On his return from studying in Italy he was admitted to the refounded Académie de peinture et de sculpture on 24 November 1731. His morceau de réception was his Rinaldo and Armida of 1734. Boucher married Marie-Jeanne Buzeau in 1733. The couple had three children together. Boucher became a faculty member in 1734 and his career accelerated from this point as he was promoted Professor then Rector of the Academy, becoming inspector at the Royal Gobelins Manufactory and finally Premier Peintre du Roi in 1765. Boucher died on 30 May 1770 in his native Paris. His name, along with that of his patron Madame de Pompadour, had become synonymous with the French Rococo style, leading the Goncourt brothers to write: Boucher is one of those men who represent the taste of a century, who express, personify and embody it. Boucher is famous for saying that nature is trop verte et mal éclairée. Boucher was associated with the gemstone engraver Jacques Guay, whom he taught to draw. He also mentored the Moravian-Austrian painter Martin Ferdinand Quadal as well as the neoclassical painter Jacques-Louis David in 1767. Later, Boucher made a series of drawings of works by Guay which Madame de Pompadour then engraved and distributed as a handsomely bound volume to favored courtiers. Boucher took inspiration from artists such as Peter Paul Rubens and Antoine Watteau. Boucher's early works celebrate the idyllic and tranquil portrayal of nature and landscape with great elan. However, his art typically forgoes traditional rural innocence to portray scenes with a definitive style of eroticism as his mythological scenes are passionate and intimately amorous rather than traditionally epic. Boucher's paintings of a flirtatious shepherd and shepherdess in a woodland setting, featured in The Enjoyable Lesson of 1748 and An Autumn Pastoral of 1749, were based upon characters in a 1745 play by Boucher's close friend Charles-Simon Favart. Boucher's characters in those paintings later inspired a pair of figurines created by the Sèvres Porcelain Manufactory, c. 1757-66. Marquise de Pompadour, whose name became synonymous with Rococo art, was a great admirer of his work. Marquise de Pompadour is often referred to as the godmother of Rococo and Boucher's portraits were central to her self-presentation and cultivation of her image. For instance, Boucher's 'Sketch for a Portrait of Madame de Pompadour', displayed in the Starhemburg room at Waddesdon Manor, acts as a surviving example of the oil preparation prior to the, now lost, portrait. In one hand she holds her hat, in the other she picks up a pearl bracelet with a portrait of the king-symbolising the relationship upon which her status depends. Boucher's paintings such as The Breakfast, a familial scene, show how he was as a master of the genre scene, where he regularly used his own wife and children as models. These intimate family scenes are contrasting to the licentious style seen in his Odalisque portraits. The dark-haired version of the Odalisque portraits prompted claims by the art critic Denis Diderot that Boucher was prostituting his own wife, and the Blonde Odalisque was a portrait that illustrated the extramarital relationships of the King. Boucher gained lasting notoriety through such private commissions for wealthy collectors and, after Diderot expressed his disapproval, his reputation came under increasing critical attack during the last years of his career. Along with his painting, Boucher also designed theater costumes and sets, and the ardent intrigues of the comic operas of Charles Simon Favart closely paralleled his own style of painting. Tapestry design was also a concern.
more...