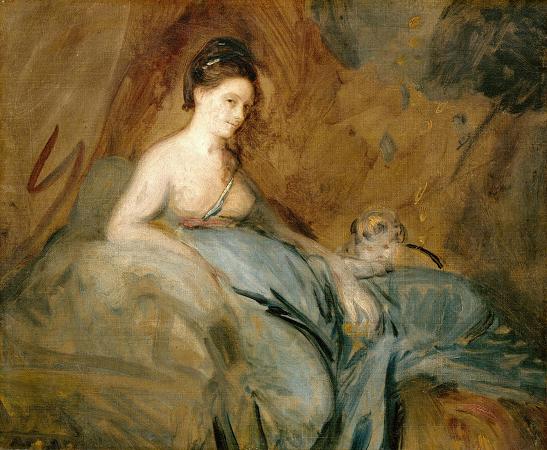Kitty Fisher (1741 - 1767). Kitty Fisher was a prominent British courtesan. From her teen years onwards, Fisher carefully developed her public image, which was boosted by attention from Sir Joshua Reynolds and other artists. By emphasizing Fisher's beauty, audacity, and charm, portraits and newspaper and magazine articles promoted her reputation and prompted spectators to view her with redoubled awe. She was one of the world's first celebrities famous not for being an actress, musician or member of the royalty, but simply for being famous. Her life exemplifies the emergence of mass media publishing and fame in an era when capitalism, commercialism, global markets, and rising emphasis on public opinion were transforming England. Born Catherine Marie Fischer, she was, according to some sources, originally a milliner, whom either Commodore Augustus Keppel or perhaps Lieutenant-General Anthony George Martin reportedly introduced to London high life. With a flair for publicity, she became known for her affairs with men of wealth. Her appearance and dress were scrutinized and copied, scurrilous broadsheets and satires upon her were printed and circulated, and several portraits of her by Reynolds, including one in which she posed as Cleopatra Dissolving the Pearl were engraved. Prints from these engravings were sold to thousands of her fans, making Kitty Fisher one of the first pin-up glamour girls. In one famous incident, Fisher fell off her horse while riding in a public park. Scores of broadsheets, ballads, and prints mocked her, playing on the pun of being a fallen woman. But Kitty was not one to be outdone and immediately seized public attention for her own ends by having her portrait painted by Joshua Reynolds, the most prominent painter in England. Her fame spread throughout Europe. When he visited London in 1763, the famous Italian lover Giacomo Casanova met Fisher and wrote:. the illustrious Kitty Fisher, who was just beginning to be fashionable. She was magnificently dressed, and it is no exaggeration to say that she had on diamonds worth five hundred thousand francs. Goudar told me that if I liked I might have her then and there for ten guineas. I did not care to do so, however, for, though charming, she could only speak English, and I liked to have all my senses, including that of hearing, gratified. When she had gone, Mrs Wells told us that Kitty had eaten a bank-note for a thousand guineas, on a slice of bread and butter, that very day. The note was a present from Sir Akins, brother of the fair Mrs Pitt. I do not know whether the bank thanked Kitty for the present she had made it. It is unclear to what extent Casanova's account is to be trusted, as similar stories of a currency or bank-note sandwich were told about several other women who were Fisher's contemporaries. His insistence that Kitty spoke only English is contradicted by other sources. It is possible Casanova sought to link his name to Kitty's due to her celebrity. Kitty maintained a famous rivalry with Maria Gunning, who had become Lady Coventry after a calculated insertion into the marriage market orchestrated by Gunning's mother. Kitty's rumored affair with Lord Coventry several years later sparked the rivalry. Giustiniana Wynne, visiting London at the time, wrote: The other day they ran into each other in the park and Lady Coventry asked Kitty the name of the dressmaker who had made her dress. Kitty Fisher answered she had better ask Lord Coventry as he had given her the dress as a gift. The altercation continued with Lady Coventry calling her an impertinent woman, and Kitty replying that she would have to accept this insult because Maria became her 'social superior' on marrying Lord Coventry, but she was going to marry a Lord herself just to be able to answer back. Kitty's retort to Lady Coventry shows her intentions to marry a Lord and thus ascend social class by means of marriage, in much the same way as Gunning herself. Kitty's cynical assessment of the gender politics of the day shows an awareness of the constraints on single women with a mind towards greater social mobility, but also serves as a condemnation of the Gunning girls for positioning themselves to marry wealthy, powerful men, merely for their own means and preservation. Wynne also wrote that: She lives in the greatest possible splendor, spends twelve thousand pounds a year, and she is the first of her social class to employ liveried servants — she even has liveried chaise porters. The first artist known to have painted her was Joshua Reynolds. In addition to the portraits made famous through engraved prints that were marketed directly to the public, he did several other painting of Fisher that suggest a more intimate, private view.
more...