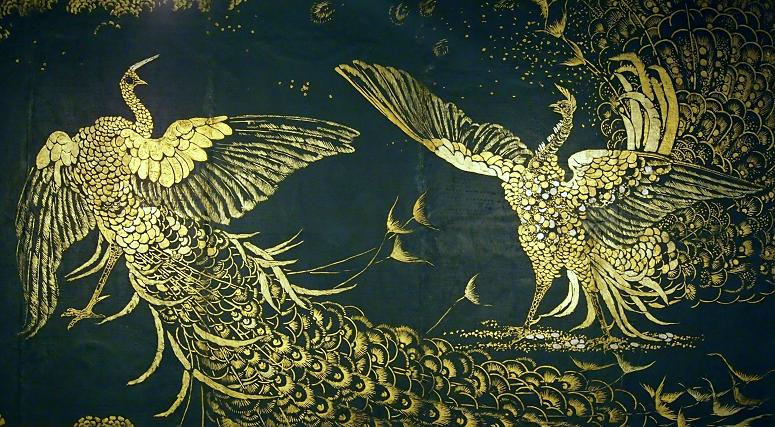
Freer Gallery of Art. The Freer Gallery of Art is an art museum of the Smithsonian Institution in Washington, D.C. focusing on Asian art. The Freer and the Arthur M. Sackler Gallery together form the Smithsonian's national museums of Asian art in the United States. The Freer and Sackler galleries house the largest Asian art research library in the country and contain art from East Asia, South Asia, Southeast Asia, the Islamic world, the ancient Near East, and ancient Egypt, as well as a significant collection of American art. The gallery is located on the south side of the National Mall in Washington, D.C., contiguous with the Sackler Gallery. The museum is open 364 days a year, and is administered by a single staff with the Sackler Gallery. The galleries are among the most visited art museums in the world. The Freer houses over 26,000 objects spanning 6,000 years of history from the Neolithic to modern eras. The collections include ancient Egyptian stone sculpture and wooden objects, ancient Near Eastern ceramics and metalware, Chinese paintings and ceramics, Korean pottery and porcelain, Japanese folding screens, Persian manuscripts, and Buddhist sculpture. In addition to Asian art, the Freer also contains the famous Harmony in Blue and Gold: The Peacock Room by American artist James McNeill Whistler which serves as the centerpiece to the Freer's American art collection. The museum offers free tours to the public and presents a full schedule events for the public including films, lectures, symposia, concerts, performances, and discussions. Over 11,000 objects from the FreerSackler collections are fully searchable and available online. The Freer was also featured in the Google Art Project, which offers online viewers close-up views of selected items from the Freer. The gallery was founded by Detroit railroad-car manufacturer and self-taught connoisseur Charles Lang Freer. He owned the largest collection of works by American artist James McNeill Whistler and became a patron and friend of the famously irascible artist. Whistler made it very clear to Freer that if he helped him to build the premier Whistler collection, then that collection would have to be displayed in a city where tourists went. In 1908, Charles Moore, a former aide to Michigan United States Senator, James McMillin and the chairman of the United States Commission of Fine Arts, moved from Washington, D.C., to Detroit. Moore became friends with Freer, who was director of the Michigan Car Company, and persuaded Freer to permanently exhibit his 8,000-piece collection of Oriental art in Washington, D.C. Before then, Freer informally proposed to President Theodore Roosevelt that he give to the nation his art collection, funds to construct a building, and an endowment fund to provide for the study and acquisition of very fine examples of Oriental, Egyptian, and Near Eastern fine arts. The Freer gift was accepted on behalf of the government by the Smithsonian Board of Regents in 1906. Freer's will, however, contained certain requirements that only objects from the permanent collection could be exhibited in the gallery, and that none of the art could be exhibited elsewhere. Freer felt strongly that all of the museum's holding should be readily accessible to scholars at all times. In addition, Freer's bequest to the Smithsonian came with the proviso that he would execute full curatorial control over the collection until his death. The Smithsonian initially hesitated at the requirements but the intercession of President Theodore Roosevelt allowed for the project to proceed. The Freer Gallery possesses an autographed letter from Roosevelt inviting Freer to visit him at the White House, reflecting the personal interest Roosevelt showed in the development of the museum. Freer died before the art gallery was completed. Construction of the gallery began in 1916 and was completed in 1921, after a delay due to World War I. On May 9, 1923, the Freer Gallery of Art was opened to the public. Designed by American architect and landscape planner Charles A. Platt, the Freer is an Italian Renaissance-style building inspired by Freer's visits to palazzos in Italy. It is reported that in a meeting with architect Charles Platt at the Plaza Hotel in New York City, Freer jotted down his ideas for a classical, well-proportioned building on a napkin. The gallery is constructed primarily of granite: the exterior of the Freer is pink granite quarried in Milford, Massachusetts, the courtyard has a carnelian granite fountain and walls of unpolished Tennessee white marble. The gallery's interior walls are Indiana limestone, and the floors are polished Tennessee marble.
more...