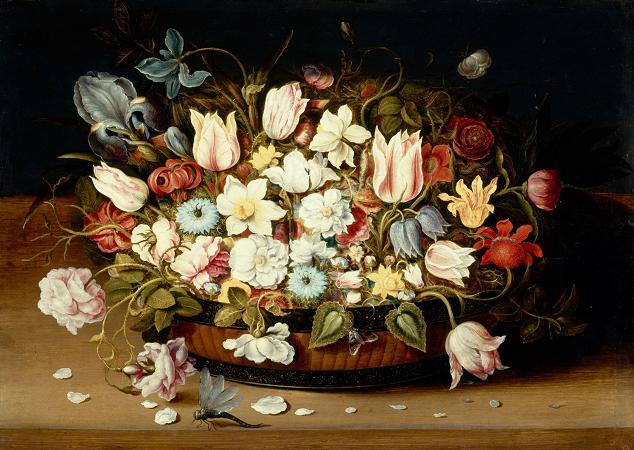
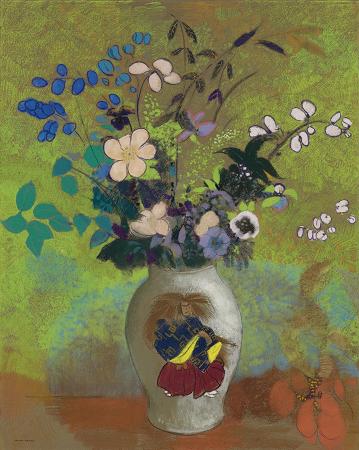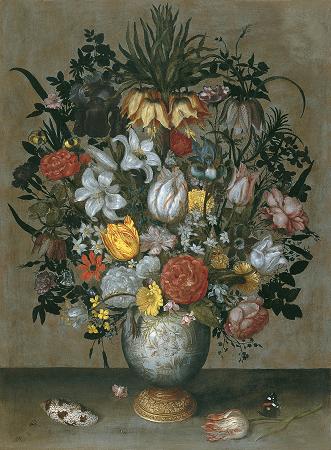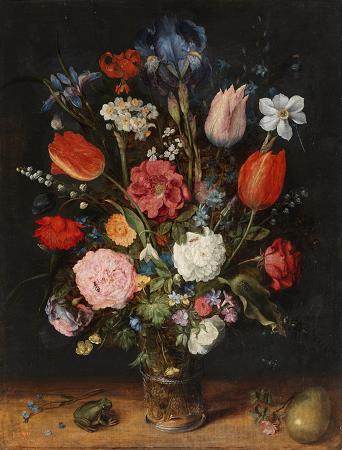Still Life with Flowers. A flower, sometimes known as a bloom or blossom, is the reproductive structure found in flowering plants. The biological function of a flower is to affect reproduction, usually by providing a mechanism for the union of sperm with eggs. Flowers may facilitate outcrossing or allow selfing. Some flowers produce diaspores without fertilization. Flowers contain sporangia and are the site where gametophytes develop. Many flowers have evolved to be attractive to animals, so as to cause them to be vectors for the transfer of pollen. After fertilization, the ovary of the flower develops into fruit containing seeds. In addition to facilitating the reproduction of flowering plants, flowers have long been admired and used by humans to bring beauty to their environment, and also as objects of romance, ritual, religion, medicine and as a source of food. The essential parts of a flower can be considered in two parts: the vegetative part, consisting of petals and associated structures in the perianth, and the reproductive or sexual parts. A stereotypical flower consists of four kinds of structures attached to the tip of a short stalk. Each of these kinds of parts is arranged in a whorl on the receptacle. Collectively the calyx and corolla form the perianth. Calyx: the outermost whorl consisting of units called sepals; these are typically green and enclose the rest of the flower in the bud stage, however, they can be absent or prominent and petal-like in some species. Corolla: the next whorl toward the apex, composed of units called petals, which are typically thin, soft and colored to attract animals that help the process of pollination. The carpel or multiple fused carpels form a hollow structure called an ovary, which produces ovules internally. Ovules are megasporangia and they in turn produce megaspores by meiosis which develop into female gametophytes. These give rise to egg cells. The gynoecium of a flower is also described using an alternative terminology wherein the structure one sees in the innermost whorl is called a pistil. A pistil may consist of a single carpel or a number of carpels fused together. The sticky tip of the pistil, the stigma, is the receptor of pollen. The supportive stalk, the style, becomes the pathway for pollen tubes to grow from pollen grains adhering to the stigma. The relationship to the gynoecium on the receptacle is described as hypogynous, perigynous, or epigynous. Although the arrangement described above is considered typical, plant species show a wide variation in floral structure. These modifications have significance in the evolution of flowering plants and are used extensively by botanists to establish relationships among plant species. The four main parts of a flower are generally defined by their positions on the receptacle and not by their function. Many flowers lack some parts or parts may be modified into other functions and/or look like what is typically another part. In some families, like Ranunculaceae, the petals are greatly reduced and in many species the sepals are colorful and petal-like. Other flowers have modified stamens that are petal-like; the double flowers of Peonies and Roses are mostly petaloid stamens. Flowers show great variation and plant scientists describe this variation in a systematic way to identify and distinguish species. Specific terminology is used to describe flowers and their parts. Many flower parts are fused together; fused parts originating from the same whorl are connate, while fused parts originating from different whorls are adnate; parts that are not fused are free. When petals are fused into a tube or ring that falls away as a single unit, they are sympetalous. Connate petals may have distinctive regions: the cylindrical base is the tube, the expanding region is the throat and the flaring outer region is the limb. A sympetalous flower, with bilateral symmetry with an upper and lower lip, is bilabiate. Flowers with connate petals or sepals may have various shaped corolla or calyx, including campanulate, funnelform, tubular, urceolate, salverform or rotate.
more...