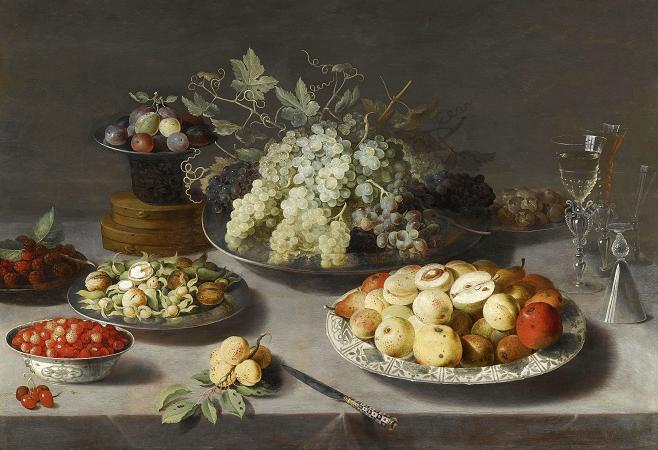
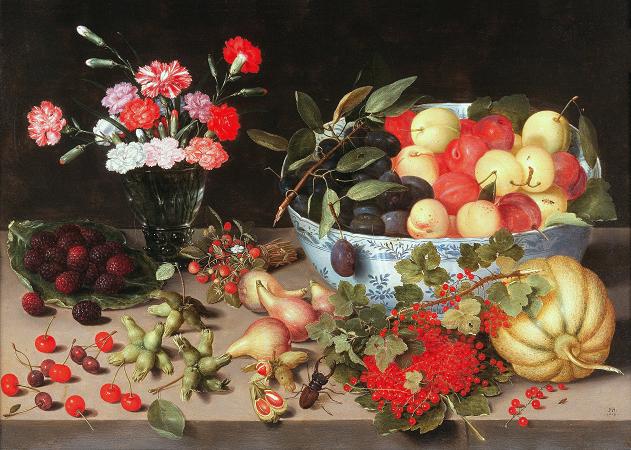
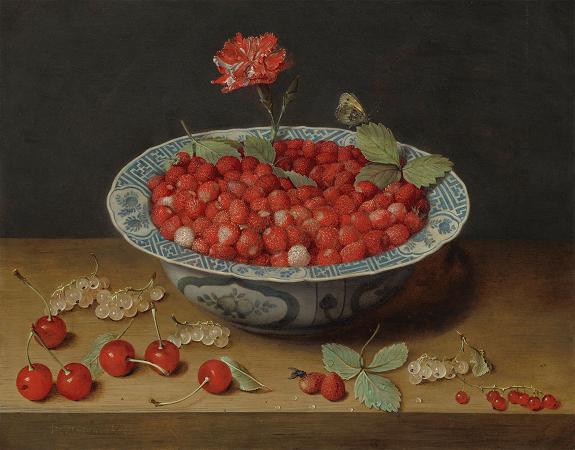
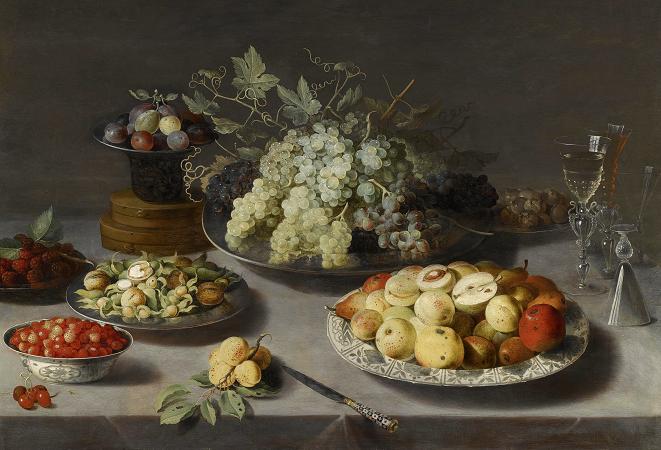
Still Life with Fruit. In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants formed from the ovary after flowering. Fruits are the means by which angiosperms disseminate seeds. Edible fruits, in particular, have propagated with the movements of humans and animals in a symbiotic relationship as a means for seed dispersal and nutrition; in fact, humans and many animals have become dependent on fruits as a source of food. Accordingly, fruits account for a substantial fraction of the world's agricultural output, and some have acquired extensive cultural and symbolic meanings. In common language usage, fruit normally means the fleshy seed-associated structures of a plant that are sweet or sour, and edible in the raw state, such as apples, bananas, grapes, lemons, oranges, and strawberries. On the other hand, in botanical usage, fruit includes many structures that are not commonly called fruits, such as bean pods, corn kernels, tomatoes, and wheat grains. The section of a fungus that produces spores is also called a fruiting body. Many common terms for seeds and fruit do not correspond to the botanical classifications. In culinary terminology, a fruit is usually any sweet-tasting plant part, especially a botanical fruit; a nut is any hard, oily, and shelled plant product; and a vegetable is any savory or less sweet plant product. However, in botany, a fruit is the ripened ovary or carpel that contains seeds, a nut is a type of fruit and not a seed, and a seed is a ripened ovule. Examples of culinary vegetables and nuts that are botanically fruit include corn, cucurbits, eggplant, legumes, sweet pepper, and tomato. In addition, some spices, such as allspice and chili pepper, are fruits, botanically speaking. In contrast, rhubarb is often referred to as a fruit, because it is used to make sweet desserts such as pies, though only the petiole of the rhubarb plant is edible, and edible gymnosperm seeds are often given fruit names, e.g., ginkgo nuts and pine nuts. Botanically, a cereal grain, such as corn, rice, or wheat, is also a kind of fruit, termed a caryopsis. However, the fruit wall is very thin and is fused to the seed coat, so almost all of the edible grain is actually a seed. Main article: Fruit anatomy The outer, often edible layer, is the pericarp, formed from the ovary and surrounding the seeds, although in some species other tissues contribute to or form the edible portion. The pericarp may be described in three layers from outer to inner, the epicarp, mesocarp and endocarp. Fruit that bears a prominent pointed terminal projection is said to be beaked. A fruit results from maturation of one or more flowers, and the gynoecium of the flower forms all or part of the fruit. Inside the ovary/ovaries are one or more ovules where the megagametophyte contains the egg cell. After double fertilization, these ovules will become seeds. The ovules are fertilized in a process that starts with pollination, which involves the movement of pollen from the stamens to the stigma of flowers. After pollination, a tube grows from the pollen through the stigma into the ovary to the ovule and two sperm are transferred from the pollen to the megagametophyte. Within the megagametophyte one of the two sperm unites with the egg, forming a zygote, and the second sperm enters the central cell forming the endosperm mother cell, which completes the double fertilization process. Later the zygote will give rise to the embryo of the seed, and the endosperm mother cell will give rise to endosperm, a nutritive tissue used by the embryo. As the ovules develop into seeds, the ovary begins to ripen and the ovary wall, the pericarp, may become fleshy, or form a hard outer covering. In some multiseeded fruits, the extent to which the flesh develops is proportional to the number of fertilized ovules. The pericarp is often differentiated into two or three distinct layers called the exocarp, mesocarp, and endocarp. In some fruits, especially simple fruits derived from an inferior ovary, other parts of the flower, fuse with the ovary and ripen with it. In other cases, the sepals, petals and/or stamens and style of the flower fall off. When such other floral parts are a significant part of the fruit, it is called an accessory fruit. Since other parts of the flower may contribute to the structure of the fruit, it is important to study flower structure to understand how a particular fruit forms. There are three general modes of fruit development: Apocarpous fruits develop from a single flower having one or more separate carpels, and they are the simplest fruits.
more...