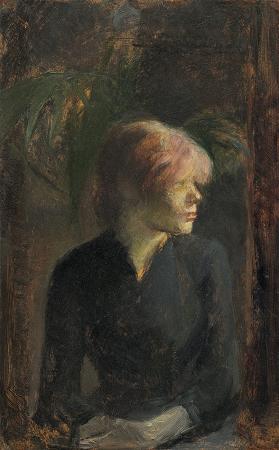Oil Paint. Oil paint is a type of slow-drying paint that consists of particles of pigment suspended in a drying oil, commonly linseed oil. It is a versatile art material favored by many artists for its rich texture, vibrant colors, and blending capabilities. Made from pigments suspended in a drying oil, typically linseed oil, it allows for a wide range of techniques and effects. Artists can apply oil paint in thick, impasto layers for a textured finish or use it in thin glazes for transparent, luminous effects. The slow drying time of oil paint enables artists to work on their pieces over extended periods, allowing for detailed blending and layering. It also facilitates the use of techniques like scumbling and glazing, which enhance depth and luminosity. Oil paint can be applied to various surfaces, including canvas, wood, and metal, and can be mixed with mediums to alter its consistency, drying time, and sheen. Additionally, oil paint has a historical significance in Western art, used by masters such as Rembrandt and Van Gogh, making it a staple in both traditional and contemporary artistic practices. For several centuries the oil painting has been perhaps the most prestigious form in Western art, but oil paint has many practical uses, mainly because it is waterproof. The earliest surviving examples of oil paint have been found in Asia from as early as the 7th century AD, in examples of Buddhist paintings in Afghanistan; the technique was perhaps not invented there. Oil-based paints made their way to Europe by the 12th century and were used for simple decoration, mostly on wood, but oil painting did not begin to be adopted as an artistic medium there until the early 15th century. Common modern applications of oil paint are in finishing and protection of wood in buildings and exposed metal structures such as ships and bridges. Its hard-wearing properties and luminous colors make it desirable for both interior and exterior use on wood and metal. Due to its slow-drying properties, it has recently been used in paint-on-glass animation. The thickness of the coat has considerable bearing on the time required for drying: thin coats of oil paint dry relatively quickly. The viscosity of the paint may be modified by the addition of a solvent such as turpentine or white spirit, and varnish may be added to increase the glossiness of the dried oil paint film. The addition of oil or alkyd medium can also be used to modify the viscosity and drying time of oil paint. The technical history of the introduction and development of oil paint, and the date of introduction of various additives is still, despite intense research since the mid 19th century, not well understood.
more...