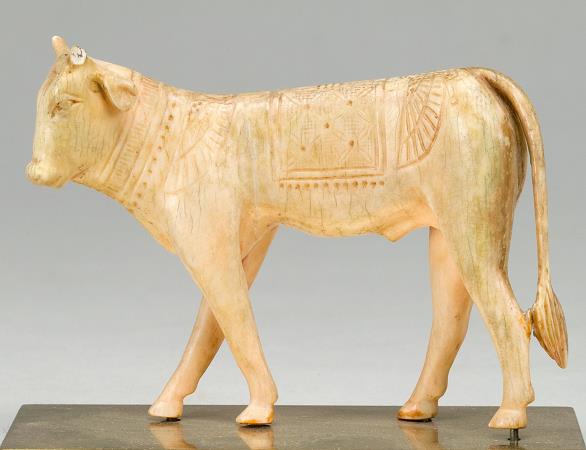
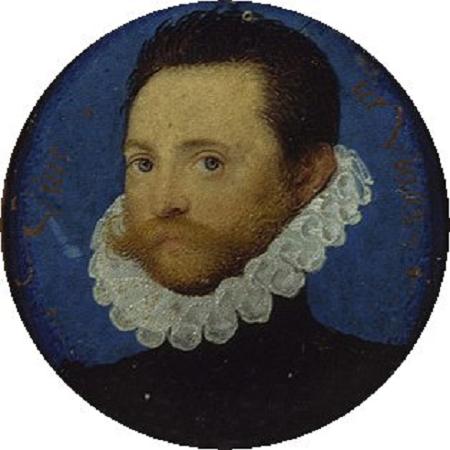
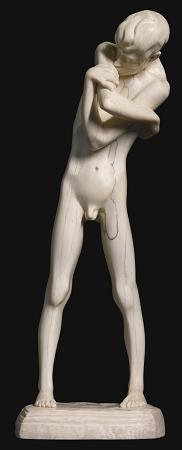
Ivory. Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals is the same, regardless of the species of origin, but ivory contains structures of mineralised collagen. The trade in certain teeth and tusks other than elephant is well established and widespread; therefore, ivory can correctly be used to describe any mammalian teeth or tusks of commercial interest which are large enough to be carved or scrimshawed. Besides natural ivory, ivory can also be produced synthetically, hence not requiring the retrieval of the material from animals. Tagua nuts can also be carved like ivory. The trade of finished goods of ivory products has its origins in the Indus Valley. Ivory is a main product that is seen in abundance and was used for trading in Harappan civilization. Finished ivory products that were seen in Harappan sites include kohl sticks, pins, awls, hooks, toggles, combs, game pieces, dice, inlay and other personal ornaments. Ivory has been valued since ancient times in art or manufacturing for making a range of items from ivory carvings to false teeth, piano keys, fans, and dominoes. Elephant ivory is the most important source, but ivory from mammoth, walrus, hippopotamus, sperm whale, orca, narwhal and warthog are used as well. Elk also have two ivory teeth, which are believed to be the remnants of tusks from their ancestors. The national and international trade in natural ivory of threatened species such as African and Asian elephants is illegal. The word ivory ultimately derives from the ancient Egyptian, through the Latin or. Main article: Ivory carving A depiction of the Blessed Virgin Mary and the Child Jesus crafted in elephant ivory An ivory tabernacle featuring the Madonna of Caress, France Both the Greek and Roman civilizations practiced ivory carving to make large quantities of high value works of art, precious religious objects, and decorative boxes for costly objects. Ivory was often used to form the white of the eyes of statues. There is some evidence of either whale or walrus ivory used by the ancient Irish. Solinus, a Roman writer in the 3rd century claimed that the Celtic peoples in Ireland would decorate their sword-hilts with the 'teeth of beasts that swim in the sea'. Adomnan of Iona wrote a story about St Columba giving a sword decorated with carved ivory as a gift that a penitent would bring to his master so he could redeem himself from slavery. The Syrian and North African elephant populations were reduced to extinction, probably due to the demand for ivory in the Classical world. The Chinese have long valued ivory for both art and utilitarian objects. Early reference to the Chinese export of ivory is recorded after the Chinese explorer Zhang Qian ventured to the west to form alliances to enable the eventual free movement of Chinese goods to the west; as early as the first century BC, ivory was moved along the Northern Silk Road for consumption by western nations. Southeast Asian kingdoms included tusks of the Indian elephant in their annual tribute caravans to China. Chinese craftsmen carved ivory to make everything from images of deities to the pipe stems and end pieces of opium pipes. In Japan, ivory carvings became popular in the 17th century during the Edo period, and many netsuke and kiseru, on which animals and legendary creatures were carved, and inro, on which ivory was inlaid, were made. From the mid-1800s, the new Meiji government's policy of promoting and exporting arts and crafts led to the frequent display of elaborate ivory crafts at World's fair. Among them, the best works were admired because they were purchased by Western museums, wealthy people, and the Japanese Imperial Family. The Buddhist cultures of Southeast Asia, including Myanmar, Thailand, Laos and Cambodia, traditionally harvested ivory from their domesticated elephants. Ivory was prized for containers due to its ability to keep an airtight seal. It was also commonly carved into elaborate seals utilized by officials to sign documents and decrees by stamping them with their unique official seal. In Southeast Asian countries, where Muslim Malay peoples live, such as Malaysia, Indonesia and the Philippines, ivory was the material of choice for making the handles of kris daggers. In the Philippines, ivory was also used to craft the faces and hands of Catholic icons and images of saints prevalent in the Santero culture. Tooth and tusk ivory can be carved into a vast variety of shapes and objects. Examples of modern carved ivory objects are okimono, netsukes, jewelry, flatware handles, furniture inlays, and piano keys.
more...