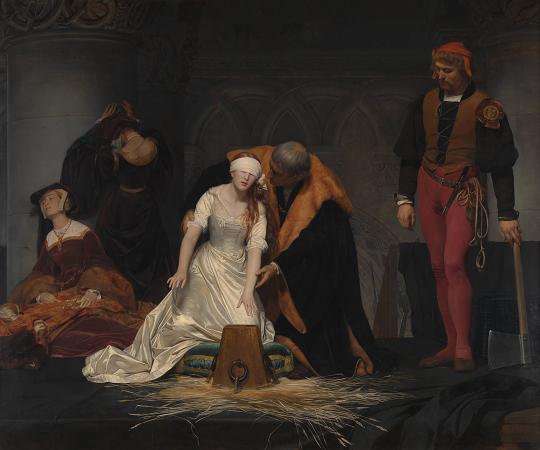
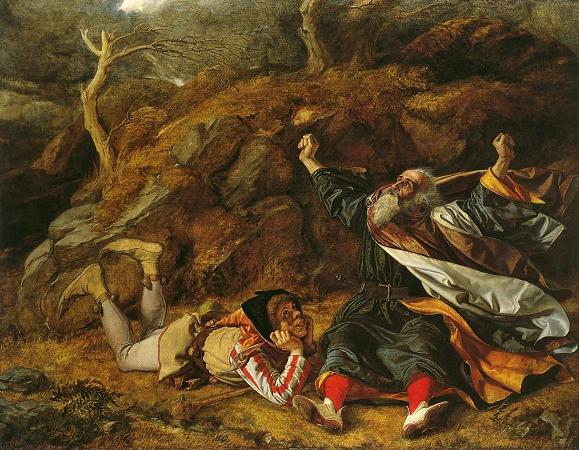
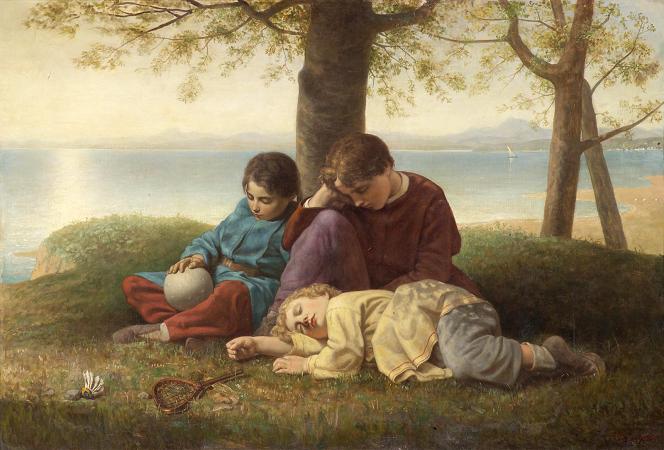
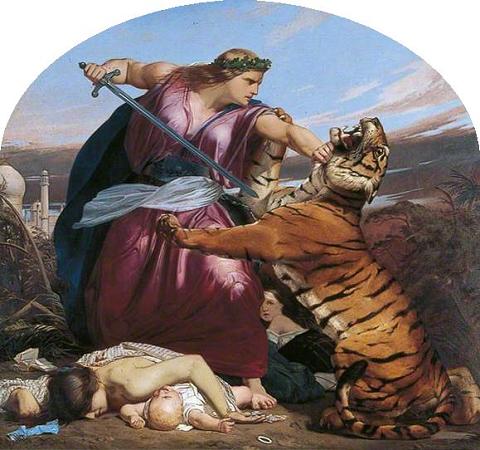
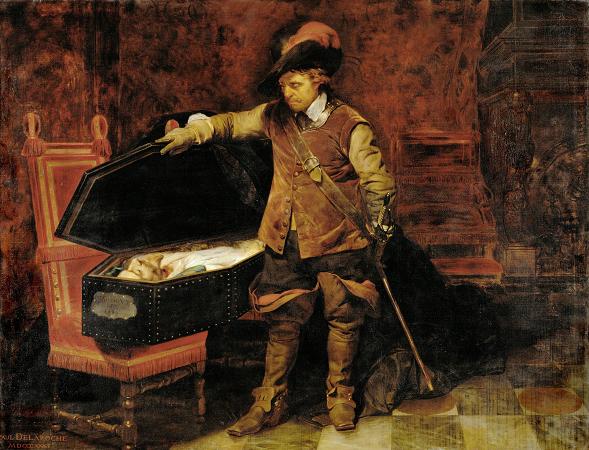
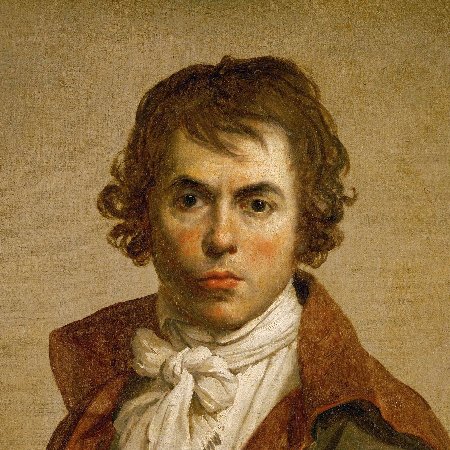
Paul Delaroche (1797 - 1856). Paul Delaroche was a French painter who achieved his greater successes painting historical scenes. He became famous in Europe for his melodramatic depictions that often portrayed subjects from English and French history. The emotions emphasised in Delaroche's paintings appeal to Romanticism while the detail of his work along with the deglorified portrayal of historic figures follow the trends of Academicism and Neoclassicism. Delaroche aimed to depict his subjects and history with pragmatic realism. He did not consider popular ideals and norms in his creations, but rather painted all his subjects in the same light whether they were historical figures, figures of Christianity, or real people of his time like Napoleon Bonaparte and Marie-Antoinette. Delaroche was a leading pupil of Antoine-Jean Gros and later mentored a number of notable artists like Thomas Couture, Jean-Léon Gérôme, and Jean-François Millet. Delaroche was born into a generation that saw the stylistic conflicts between Romanticism and Davidian Classicism. Davidian Classicism was widely accepted and enjoyed by society so as a developing artist at the time of the introduction of Romanticism in Paris, Delaroche found his place between the two movements. Subjects from Delaroche's medieval and sixteenth and seventeenth-century history paintings appealed to Romantics while the accuracy of information along with the highly finished surfaces of his paintings appealed to Academics and Neoclassicism. Delaroche's works completed in the early 1830s most reflected the position he took between the two movements and were admired by contemporary artists of the time, the Execution of Lady Jane Grey was the most acclaimed of Delaroche's paintings in its day. Later in the 1830s, Delaroche exhibited the first of his major religious works. His change of subject and the painting's austere manner were ill-received by critics and after 1837, he stopped exhibiting his work altogether. At the time of his death in 1856, he was painting a series of four scenes from the Life of the Virgin. Only one work from this series was completed: the Virgin Contemplating the Crown of Thorns. Delaroche was born in Paris and stayed there for the majority of his life. Most of his works were completed in his studio on Rue Mazarin. His subjects were painted with a firm, solid, smooth surface, which gave an appearance of the highest finish. This texture was the manner of the day and was also found in the works of Vernet, Ary Scheffer, Louis Léopold Robert and Jean Auguste Dominique Ingres. Among his students were British landscape artist Henry Mark Anthony, British history painters Edward Armitage and Charles Lucy, and American painter/photographer Alfred Boisseau. The first Delaroche picture exhibited was the large Jehosheba saving Joash. This exhibition led to his acquaintance with Théodore Géricault and Eugène Delacroix, with whom he formed the core of a large group of Parisian historical painters. He visited Italy in 1838 and 1843, when his father-in-law, Horace Vernet, was director of the French Academy in Rome. In 1845, he was elected into the National Academy of Design, New York, as an Honorary Academician. Paul Delaroche was born into the petty lord de la Roche family, a family of artists, dealers, collectors, and art administrators. His father, Gregoire-Hippolyte Delaroche, was a prominent art dealer in Paris. Paul Delaroche was the second of two sons and was introduced to fine art at a young age. At age nineteen, Delaroche was afforded by his father the opportunity to study at L'École des Beaux-Arts under the instruction of Louis Étienne Watelet. Delaroche was influenced by his father to focus on landscapes while he was at L'École because his brother, Jules-Hippolyte Delaroche, already focused on painting history. After two years at L'École, Delaroche voiced his disinterest in landscapes and acted on his overall disagreement to the French academic system. He left L'École des Beaux-Art in at the end of 1817. In the year 1818, Delaroche entered the studio of Antoine-Jean Gros where he could pursue his greater interest of history painting. Delaroche's debuted at the Salon in 1822 where he exhibited Christ Descended from the Cross and Jehosheba Saving Joash. The latter was a product of Gros's influence and was praised by Géricault who supported the beginning of Romanticism. The schooling Delaroche received at L'Ecole des Beaux-Arts tied him to the ideas of Academicism and Neo-Classicism while his time spent in the studio of Gros aroused his interest of history and its representation through Romanticism. His painting, Joan of Arc in Prison, which was exhibited in the Salon of 1824, along with his following works reflect the middle ground he occupied.
more...