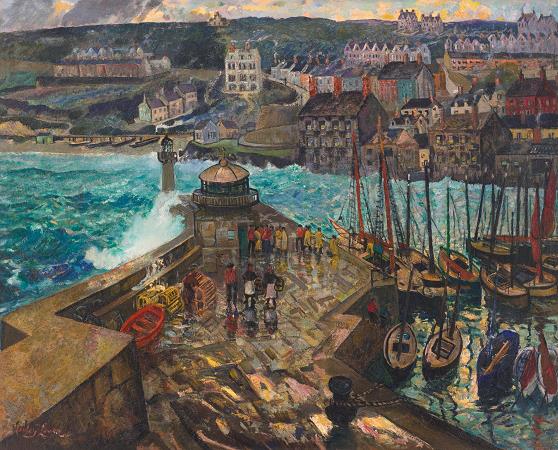
Saint Ives. St Ives is a seaside town, civil parish and port in Cornwall, England. The town lies north of Penzance and west of Camborne on the coast of the Celtic Sea. In former times it was commercially dependent on fishing. The decline in fishing, however, caused a shift in commercial emphasis, and the town is now primarily a popular seaside resort, notably achieving the title of Best UK Seaside Town from the British Travel Awards in both 2010 and 2011. St Ives was incorporated by Royal Charter in 1639. St Ives has become renowned for its number of artists. It was named best seaside town of 2007 by The Guardian newspaper. It should not be confused with St Ive, a village and civil parish in south-east Cornwall. The origin of St Ives is attributed in legend to the arrival of the Irish saint Ia of Cornwall, in the 5th century. The parish church bears her name, and the name St Ives derives from it. The Sloop Inn, which lies on the wharf was a fisherman's pub for many centuries and is dated to circa 1312, making it one of the oldest inns in Cornwall. The town was the site of a particularly notable atrocity during the Prayer Book Rebellion of 1549. The English provost marshal, Anthony Kingston, came to St Ives and invited the portreeve, John Payne, to lunch at an inn. He asked the portreeve to have the gallows erected during the course of the lunch. Afterwards the portreeve and the Provost Marshal walked down to the gallows; the Provost Marshal then ordered the portreeve to mount the gallows. The portreeve was then hanged for being a busy rebel. The seal of St Ives is Argent, an ivy branch overspreading the whole field Vert, with the legend Sigillum Burgi St. Ives in Com. Cornub. 1690. During the Spanish Armada of 1597, two Spanish ships, a bark and a pinnace, had made their way to St Ives to seek shelter from the storm which had dispersed the Spanish fleet. They were captured by the English warship Warspite of Sir Walter Raleigh leaking from the same storm. The information given by the prisoners was vital on learning the Armada's objectives. From medieval times fishing was important at St Ives; it was one of the most important fishing ports on the north Cornish coast. The original pier's construction date is unknown but the first reference to St Ives having a pier was in 1478 in William Worcester's Itinerary. The pier was re-built by John Smeaton between 1766 and 1770 after falling into disrepair. It was lengthened at a later date. The octagonal lookout with a cupola belongs to Smeaton's design. A. K. Hamilton Jenkin describes how the St Ives fisherman strictly observed Sunday as a day of rest. St Ives was a very busy fishing port and seining was the usual method of fishing. Seining was carried out by a set of three boats of different sizes, the largest two carrying seine nets of different sizes. The total number of crew was seventeen or eighteen. However this came to an end in 1924. In the decade 1747-1756 the total number of pilchards dispatched from the four principal Cornish ports of Falmouth, Fowey, Penzance, and St Ives averaged 30,000 hogsheads annually. Much greater catches were achieved in 1790 and 1796. In 1847 the exports of pilchards from Cornwall amounted to 40,883 hogsheads or 122 million fish while the greatest number ever taken in one seine was 5,600 hogsheads at St Ives in 1868. The bulk of the catch was exported to Italy: for example, in 1830, 6400 hogsheads were sent to Mediterranean ports. From 1829 to 1838, the yearly average for this trade was 9,000 hogsheads. While commercial fishing is much reduced, the harbour is still in use, often for recreational boating, tourist fishing and day trips to the nearby seal colonies on the Carrack Rocks and other locations along the coast. Recently, a class of Victorian fishing boat unique to St Ives, known as a jumbo, has been replicated by boatbuilder Jonny Nance to celebrate the town's maritime heritage. Today's jumbos are operated by the St Ives Jumbo Association. The first lifeboat was stationed in the town in 1840. In 1867 the Royal National Lifeboat Institution built a boathouse at Porthgwidden beach. It proved to be a difficult site to launch from, and in 1867 it was replaced by a building in Fore Street. In 1911 a new boathouse was built on the Quay, and then in 1993 a larger station was built at the landward end of the West Pier. Since its inception in 1839, thirty eight RNLI medals have been awarded to rescuers from St Ives, 18 silver medals and 20 bronze. Seven crewmen died in the St Ives lifeboat tragedy of 1939.
more...