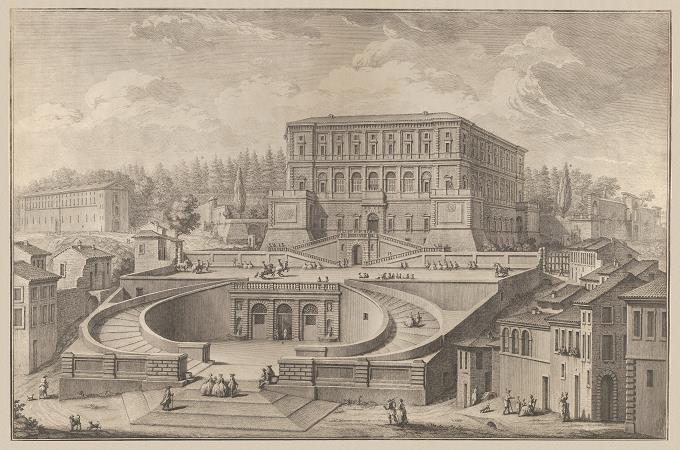
Villa Farnese. The Villa Farnese, also known as Villa Caprarola, is a mansion in the town of Caprarola in the province of Viterbo, Northern Lazio, Italy, approximately 50 kilometres north-west of Rome. This villa should not be confused with the Palazzo Farnese and the Villa Farnesina, both in Rome. A property of the Republic of Italy, Villa Farnese is run by the Polo Museale del Lazio. The Villa Farnese is situated directly above the town of Caprarola and dominates its surroundings. It is a massive Renaissance and Mannerist construction, opening to the Monte Cimini, a range of densely wooded volcanic hills. It is built on a five-sided plan in reddish gold stone; buttresses support the upper floors. As a centerpiece of the vast Farnese holdings, Caprarola has always been an expression of Farnese power, rather than a villa in the more usual agricultural or pleasure senses. In 1504, Cardinal Alessandro Farnese, the future Pope Paul III, acquired the estate at Caprarola. He had designs made for a fortified castle or rocca by the architects Antonio da Sangallo the Younger and Baldassare Peruzzi. Surviving plan drawings by Peruzzi show a pentagonal arrangement with each face of the pentagon canted inwards towards its center, to permit raking fire upon a would-be scaling force, both from the center and from the projecting bastions that advance from each corner angle of the fortress. Peruzzi's plan also shows a central pentagonal courtyard and it is likely that the later development of the circular central court was also determined by the necessities of the pentagonal plan. The pentagonal fortress foundations, constructed probably between 1515 and 1530, became the base upon which the present villa sits; so the overall form of the villa was predetermined by the rocca foundations. Subsequently, Cardinal Alessandro Farnese, a grandson of Pope Paul III, and a man who was known for promoting his family's interests, planned to turn this partly constructed fortified edifice into a villa or country house. In 1556, he commissioned Giacomo Barozzi da Vignola as his architect, building work commenced in 1559 and Vignola continued to work on the villa at Caprarola until his death in 1573. Farnese was a courteous man of letters; however, the Farnese family as a whole became unpopular with the following pope, Julius III, and, accordingly, Alessandro Farnese decided it would be politic to retire from the Vatican for a period. He therefore selected Caprarola on the family holding of Ronciglione, being both near and yet far enough from Rome as the ideal place to build a country house. For other uses, see Palazzo Farnese. The villa is one of the finest examples of Renaissance architecture. Ornament is used sparingly to achieve proportion and harmony. Thus while the villa dominates the surroundings, its severe design also complements the site. This particular style, known today as Mannerism, was a reaction to the ornate earlier High Renaissance designs of twenty years earlier. Vignola, the architect chosen for this difficult and inhospitable site, had recently proved his mettle in designing Villa Giulia on the outskirts of Rome for the preceding pope, Julius III. Vignola in his youth had been heavily influenced by Michelangelo. For the villa at Caprarola, his plans as built were for a pentagon constructed around a circular colonnaded courtyard. In the galleried court, paired Ionic columns flank niches containing busts of the Roman Emperors, above a rusticated arcade, a reworking of Bramante's scheme for the House of Raphael, in the Borgo rione, Rome. A further Bramantesque detail is the entablature that breaks forward over the columns, linking them above, while they stand on separate bases. The interior loggia formed by the arcade is frescoed with Raphaelesque grotesques, in the manner of the Vatican Logge. The gallery and upper floors were reached by five spiral staircases around the courtyard: the most important of these is the Scala Regia rising through the principal floors. The approach to the Villa Farnese is from the town's main street, which is centred on the villa, to a piazza from which stairs ascend to a series of terraces beginning with the subterranean basement excavated from the tuff, surrounded by steep curving steps leading to the terrace above. This basement floor in the foundations, which functioned as a carriage entrance in inclement weather, features a massive central column with a series of buttresses and retaining walls; on the exterior, large heavily grilled doors in the rusticated walls appear to lead into the guardrooms of a fortress, while above them a curved balustraded external double stairway leads to the terrace above.
more...