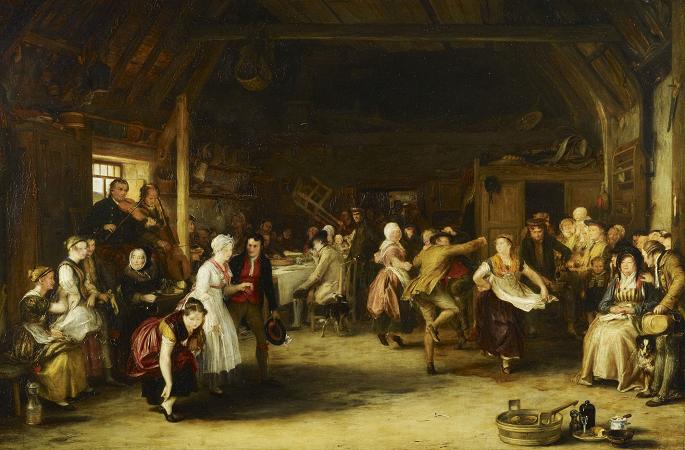
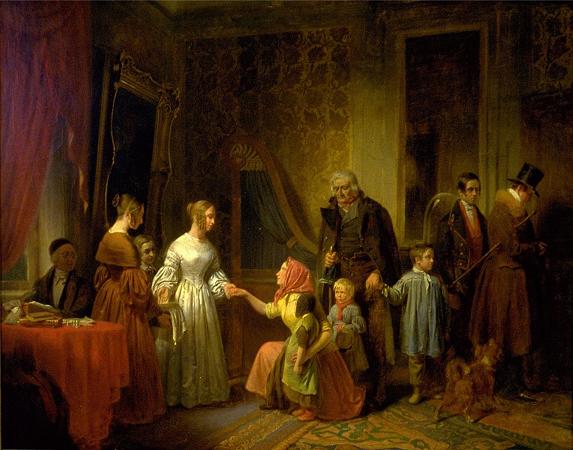
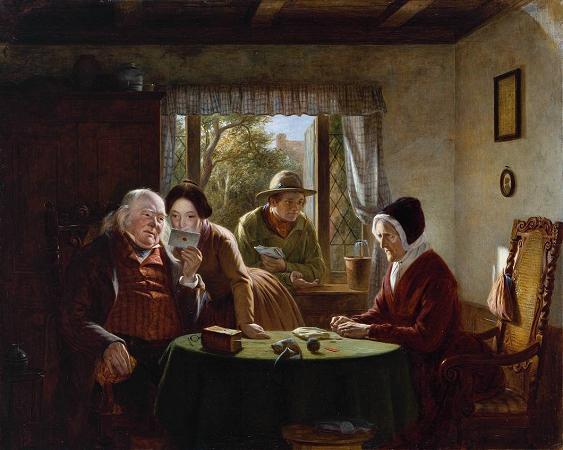
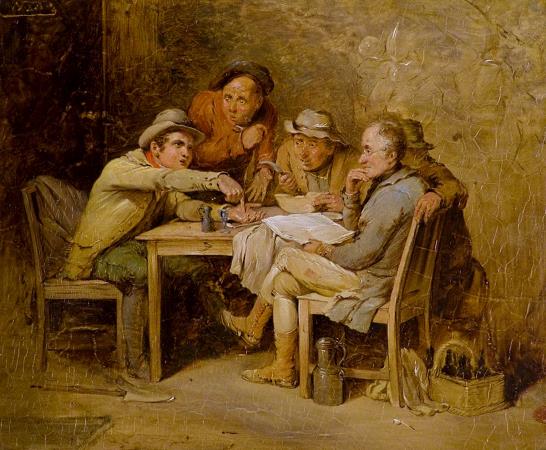
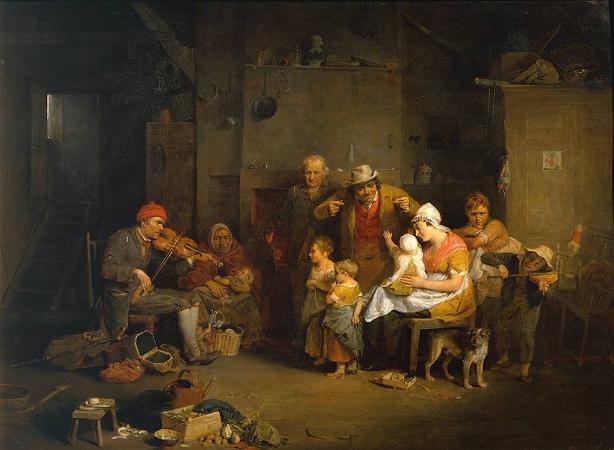
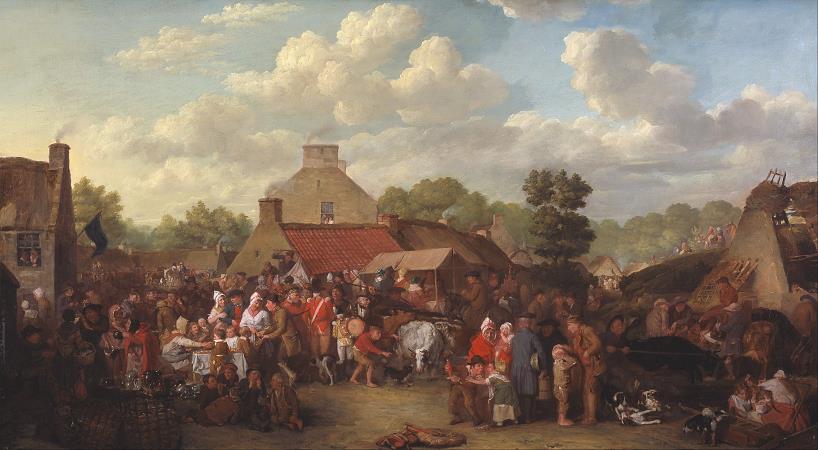David Wilkie (1785 - 1841). Sir David Wilkie was a British painter, especially known for his genre scenes. He painted successfully in a wide variety of genres, including historical scenes, portraits, including formal royal ones, and scenes from his travels to Europe and the Middle East. His main base was in London, but he died and was buried at sea, off Gibraltar, returning from his first trip to the Middle East. He was sometimes known as the people's painter. He was Principal Painter in Ordinary to King William IV and Queen Victoria. Apart from royal portraits, his best-known painting today is probably The Chelsea Pensioners reading the Waterloo Dispatch of 1822 in Apsley House. David Wilkie was born in Pitlessie Fife in Scotland on 18 November 1785. He was the son of the parish minister of Cults, Fife. Caroline Wilkie was a relative. He developed a love for art at an early age. In 1799, after he had attended school at Pitlessie, Kingskettle and Cupar, his father reluctantly agreed to his becoming a painter. Through the influence of the Earl of Leven Wilkie was admitted to the Trustees' Academy in Edinburgh, and began the study of art under John Graham. From William Allan and John Burnet, the engraver of Wilkie's works, we have an interesting account of his early studies, of his indomitable perseverance and power of close application, of his habit of haunting fairs and marketplaces, and transferring to his sketchbook all that struck him as characteristic and telling in figure or incident, and of his admiration for the works of Alexander Carse and David Allan, two Scottish painters of scenes from humble life. Among his pictures of this period might be mentioned a subject from Macbeth, Ceres in Search of Proserpine, and Diana and Calisto, which in 1803 gained a premium of ten guineas at the Trustees' Academy, while his pencil portraits of himself and his mother, dated that year, and now in the possession of the Duke of Buccleuch, prove that Wilkie had already attained considerable certainty of touch and power of rendering character. A scene from Allan Ramsay, and a sketch from Hector Macneill's ballad Scotland's Skaith, afterwards developed into the well-known Village Politicians. In 1804, Wilkie left the Trustees' Academy and returned to Cults. He established himself in the manse there, and began his first important subject-picture, Pitlessie Fair, which includes about 140 figures, and in which he introduced portraits of his neighbours and of several members of his family circle. In addition to this elaborate figure-piece, Wilkie was much employed at the time upon portraits, both at home and in Kinghorn, St Andrews and Aberdeen. In the spring of 1805 he left Scotland for London, carrying with him his Bounty-Money, or the Village Recruit, which he soon disposed of for E6, and began to study in the schools of the Royal Academy. One of his first patrons in London was Robert Stodart, a pianoforte maker, a distant connection of the Wilkie family, who commissioned his portrait and other works and introduced the young artist to the dowager countess of Mansfield. This lady's son was the purchaser of the Village Politicians, which attracted great attention when it was exhibited in the Royal Academy of 1806, where it was followed in the succeeding year by The Blind Fiddler, a commission from the painter's lifelong friend Sir George Beaumont. Wilkie now turned to historical scenes, and painted his Alfred in the Neatherd's Cottage, for the gallery illustrative of English history which was being formed by Alexander Davison. After its completion he returned to genre-painting, producing the Card-Players and the admirable picture of the Rent Day which was composed during recovery from a fever contracted in 1807 while on a visit to his native village. His next great work was the Ale-House Door, afterwards entitled The Village Festival, which was purchased by John Julius Angerstein for 800 guineas. It was followed in 1813 by the well-known Blind Man's Buff, a commission from the Prince Regent, to which a companion picture, the Penny Wedding, was added in 1818. In November 1809 he was elected an associate of the Royal Academy, when he had hardly attained the age prescribed by its laws, and in February 1811 he became a full Academician. In 1812 he opened an exhibition of his collected works in Pall Mall, but the experiment was financially unsuccessful. In 1814 he executed the Letter of Introduction, one of the most delicately finished and perfect of his cabinet pictures. In the same year he made his first visit to the continent, and in Paris entered upon a profitable and delighted study of the works of art collected in the Louvre.
more...