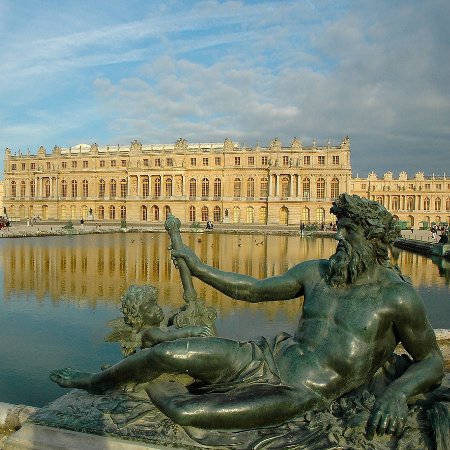
Palace of Versailles. The Palace of Versailles was the principal royal residence of France from 1682, under Louis XIV, until the start of the French Revolution in 1789, under Louis XVI. It is located in the department of Yvelines, in the region of Île-de-France, about 20 kilometres southwest of the centre of Paris. The palace is now an historical monument and UNESCO World Heritage site, notable especially for the ceremonial Hall of Mirrors, the jewel-like Royal Opera, and the royal apartments; for the more intimate royal residences, the Grand Trianon and Petit Trianon located within the park; the small rustic Hameau created for Marie Antoinette; and the vast Gardens of Versailles with fountains, canals, and geometric flower beds and groves, laid out by André le Nôtre. The Palace was stripped of all its furnishings after the French Revolution, but many pieces have been returned and many of the palace rooms have been restored. In 2017 the Palace of Versailles received 7,700,000 visitors, making it the second-most visited monument in the Île-de-France region, just behind the Louvre and ahead of the Eiffel Tower. The site of the Palace was first occupied by a small village and church, surrounded by forests filled with abundant game. It was owned by the Gondi family and the priory of Saint Julian. King Henry IV went hunting there in 1589, and returned in 1604 and 1609, staying in the village inn. His son, the future Louis XIII, came on his own hunting trip there in 1607. After he became King in 1610, Louis XIII returned to the village, bought some land, and in 1623-24 built a modest two-story hunting lodge on the site of the current marble courtyard. He was staying there in November 1630 during the event known as the Day of the Dupes, when the enemies of the King's chief minister, Cardinal Richelieu, aided by the King's mother, Marie de' Medici, tried to take over the government. The King defeated the plot and sent his mother into exile. After this event, Louis XIII decided to make his hunting lodge at Versailles into a château. The King purchased the surrounding territory from the Gondi family and in 1631-1634 had the architect Philibert Le Roy replace the hunting lodge with a château of brick and stone with classical pilasters in the doric style and high slate-covered roofs, surrounding the courtyard of the original hunting lodge. The gardens and park were also enlarged, laid out by Jacques Boyceau and his nephew, Jacques de Menours, and reached essentially the size they have today. Louis XIV first visited the château on a hunting trip in 1651 at the age of twelve, but returned only occasionally until his marriage to Maria Theresa of Spain in 1660 and the death of Cardinal Mazarin in 1661, after which he suddenly acquired a passion for the site. He decided to rebuild, embellish and enlarge the château and to transform it into a setting for both rest and for elaborate entertainments on a grand scale. The first phase of the expansion was designed and supervised by the architect Louis Le Vau. Initially he added two wings to the forecourt, one for servants quarters and kitchens, the other for stables. In 1668 he added three new wings built of stone, known as the envelope, to the north, south and west of the original château. These buildings had nearly-flat roofs covered with lead. The king also commissioned the landscape designer André Le Nôtre to create the most magnificent gardens in Europe, embellished with fountains, statues, basins, canals, geometric flower beds and groves of trees. He also added two grottos in the Italian style and an immense orangerie to house fruit trees, as well as a zoo with a central pavilion for exotic animals. After Le Vau's death in 1670, the work was taken over and completed by his assistant François d'Orbay. The main floor of the new palace contained two symmetrical sets of apartments, one for the king and the other for the queen, looking over the gardens. The two apartments were separated by a marble terrace, overlooking the garden, with a fountain in the center. Each set of apartments was connected to the ground floor with a ceremonial stairway, and each had seven rooms, aligned in a row; a vestibule, a room for the guards, an antechamber, chamber, a large cabinet or office; a smaller bedroom, and a smaller cabinet.
more...