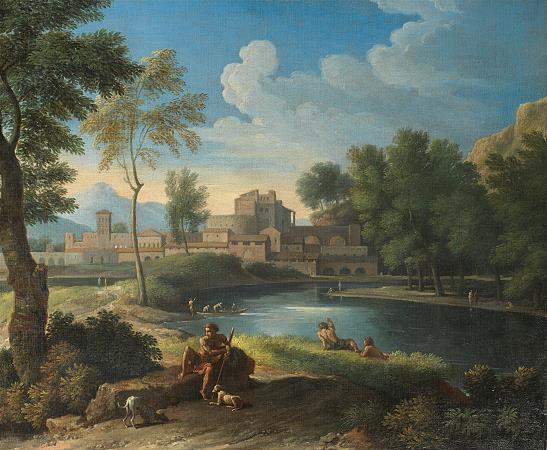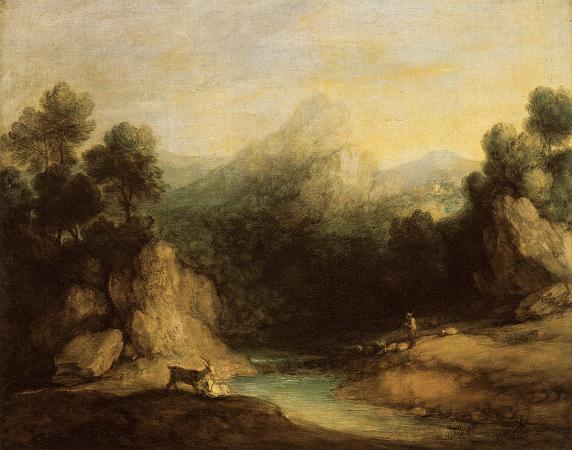Pastoral Landscape. A pastoral lifestyle is that of shepherds herding livestock around open areas of land according to seasons and the changing availability of water and pasture. It lends its name to a genre of literature, art, and music that depicts such life in an idealized manner, typically for urban audiences. A pastoral is a work of this genre, also known as bucolic, from the Greek, from, meaning a cowherd. Pastoral is a mode of literature in which the author employs various techniques to place the complex life into a simple one. Paul Alpers distinguishes pastoral as a mode rather than a genre, and he bases this distinction on the recurring attitude of power; that is to say that pastoral literature holds a humble perspective toward nature. Thus, pastoral as a mode occurs in many types of literature as well as genres. Terry Gifford, a prominent literary theorist, defines pastoral in three ways in his critical book Pastoral. The first way emphasizes the historical literary perspective of the pastoral in which authors recognize and discuss life in the country and in particular the life of a shepherd. This is summed up by Leo Marx with the phrase No shepherd, no pastoral. The second type of the pastoral is literature that describes the country with an implicit or explicit contrast to the urban. The third type of pastoral depicts the country life with derogative classifications. Hesiod's Works and Days presents a 'golden age' when people lived together in harmony with nature. This Golden Age shows that even before the Alexandrian age, ancient Greeks had sentiments of an ideal pastoral life that they had already lost. This is the first example of literature that has pastoral sentiments and may have begun the pastoral tradition. Ovid's Metamorphoses is much like the Works and Days with the description of ages but with more ages to discuss and less emphasis on the gods and their punishments. In this artificially constructed world, nature acts as the main punisher. Another example of this perfect relationship between man and nature is evident in the encounter of a shepherd and a goatherd who meet in the pastures in Theocritus' poem Idylls 1.Traditionally, pastoral refers to the lives of herdsmen in a romanticized, exaggerated, but representative way. In literature, the adjective pastoral refers to rural subjects and aspects of life in the countryside among shepherds, cowherds and other farm workers that are often romanticized and depicted in a highly unrealistic manner. The pastoral life is usually characterized as being closer to the Golden age than the rest of human life. The setting is a Locus Amoenus, or a beautiful place in nature, sometimes connected with images of the Garden of Eden. An example of the use of the genre is the short poem by the 15th-century Scottish makar Robert Henryson Robene and Makyne which also contains the conflicted emotions often present in the genre. A more tranquil mood is set by Christopher Marlowe's well known lines from his 1599 The Passionate Shepherd to His Love: Come live with me and be my Love, And we will all the pleasures prove That hills and valleys, dale and field, And all the craggy mountains yield. There will we sit upon the rocks And see the shepherds feed their flocks, By shallow rivers, to whose falls Melodious birds sing madrigals. The Passionate Shepherd to His Love exhibits the concept of Gifford's second definition of pastoral. The speaker of the poem, who is the titled shepherd, draws on the idealization of urban material pleasures to win over his love rather than resorting to the simplified pleasures of pastoral ideology. This can be seen in the listed items: lined slippers, purest gold, silver dishes, and ivory table. The speaker takes on a voyeuristic point of view with his love, and they are not directly interacting with the other true shepherds and nature. Pastoral shepherds and maidens usually have Greek names like Corydon or Philomela, reflecting the origin of the pastoral genre. Pastoral poems are set in beautiful rural landscapes, the literary term for which is locus amoenus, such as Arcadia, a rural region of Greece, mythological home of the god Pan, which was portrayed as a sort of Eden by the poets. The tasks of their employment with sheep and other rustic chores is held in the fantasy to be almost wholly undemanding and is left in the background, leaving the shepherdesses and their swains in a state of almost perfect leisure. This makes them available for embodying perpetual erotic fantasies. The shepherds spend their time chasing pretty girls or, at least in the Greek and Roman versions, pretty lads as well.
more...