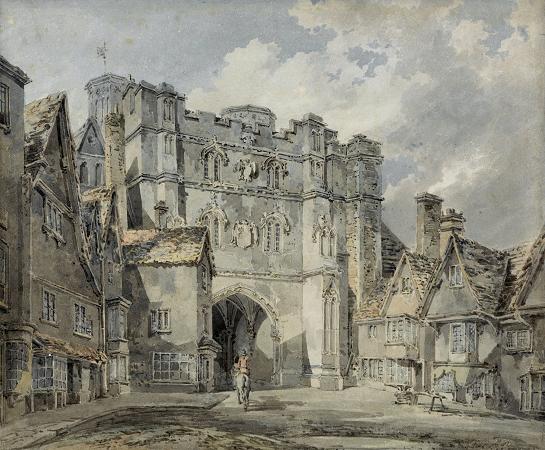
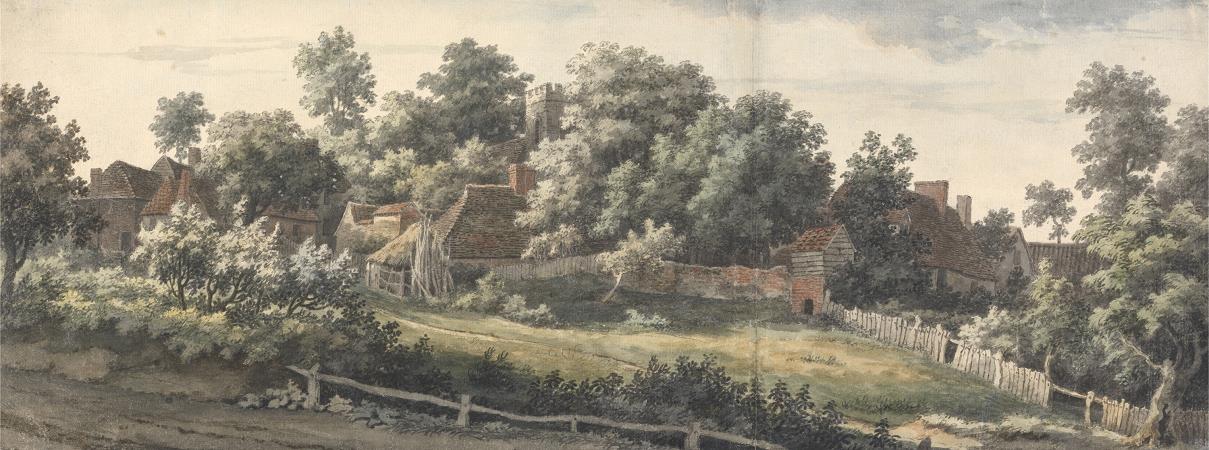
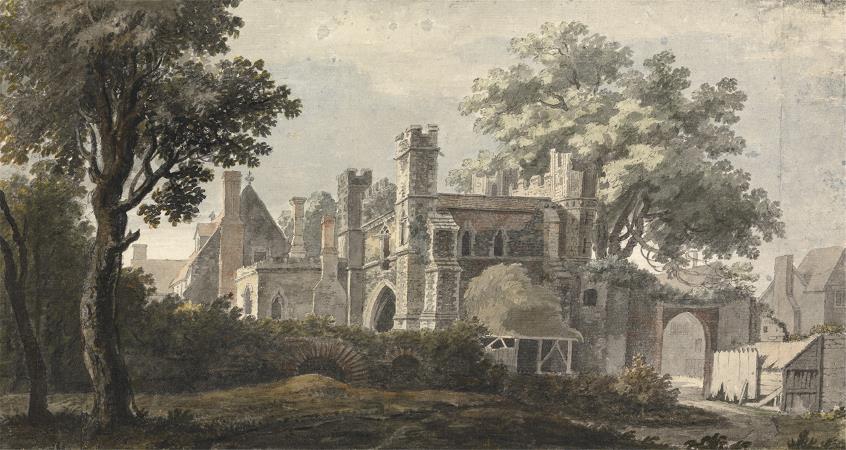
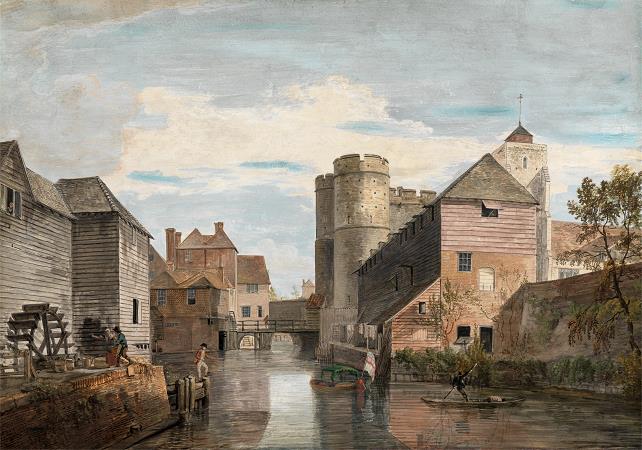
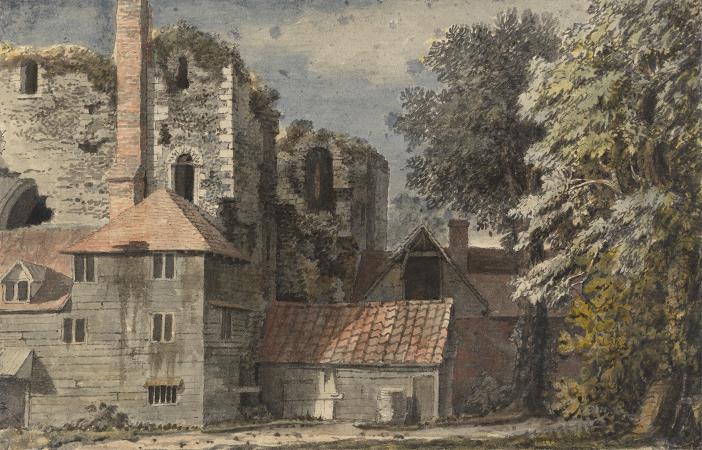Canterbury. Canterbury is a historic English cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury, a local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour. The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of the Church of England and the worldwide Anglican Communion owing to the importance of St Augustine, who served as the apostle to the pagan Kingdom of Kent around the turn of the 7th century. The city's cathedral became a major focus of pilgrimage following the 1170 martyrdom of Thomas Becket, although it had already been a well-trodden pilgrim destination since the murder of St Alphege by the men of King Canute in 1012. A journey of pilgrims to Becket's shrine served as the frame for Geoffrey Chaucer's 14th century classic The Canterbury Tales. Canterbury is a popular tourist destination: consistently one of the most-visited cities in the United Kingdom, the city's economy is heavily reliant upon tourism. The city has been occupied since Paleolithic times and served as the capital of the Celtic Cantiaci and Jute Kingdom of Kent. Many historical structures fill the area, including a city wall founded in Roman times and rebuilt in the 14th century, the ruins of St Augustine's Abbey and a Norman castle, and the oldest extant school in the world, the King's School. Modern additions include the Marlowe Theatre and the St Lawrence Ground, home of the Kent County Cricket Club. There is also a substantial student population, brought about by the presence of the University of Kent, Canterbury Christ Church University, the University for the Creative Arts, and the Girne American University Canterbury campus. Canterbury remains, however, a small city in terms of geographical size and population, when compared with other British cities. The Roman settlement of Durovernum Cantiacorum occupied the location of an earlier British town whose ancient British name has been reconstructed as Durouiernon, although the name is sometimes supposed to have derived from various British names for the Stour. In Sub-Roman Britain, it was known in Old Welsh as Cair Ceint. Occupied by the Jutes, it became known in Old English as Cantwareburh, which developed into the present name. History of Canterbury redirects here. For the history of the regional area of this name in New Zealand, see History of the Canterbury Region. Main article: Durovernum Cantiacorum The Canterbury area has been inhabited since prehistoric times. Lower Paleolithic axes, and Neolithic and Bronze Age pots have been found in the area. Canterbury was first recorded as the main settlement of the Celtic tribe of the Cantiaci, which inhabited most of modern-day Kent. In the 1st century AD, the Romans captured the settlement and named it Durovernum Cantiacorum. The Romans rebuilt the city, with new streets in a grid pattern, a theatre, a temple, a forum, and public baths. Although they did not maintain a major military garrison, its position on Watling Street relative to the major Kentish ports of Rutupiae, Dubrae, and Lemanae gave it considerable strategic importance. In the late 3rd century, to defend against attack from barbarians, the Romans built an earth bank around the city and a wall with seven gates, which enclosed an area of 130 acres. Despite being counted as one of the 28 cities of Sub-Roman Britain, it seems that after the Romans left Britain in 410 Durovernum Cantiacorum was abandoned for around 100 years, except by a few farmers and gradually decayed. Over the next 100 years, an Anglo-Saxon community formed within the city walls, as Jutish refugees arrived, possibly intermarrying with the locals. In 597, Pope Gregory the Great sent Augustine to convert its King Æthelberht to Christianity. After the conversion, Canterbury, being a Roman town, was chosen by Augustine as the centre for his episcopal see in Kent, and an abbey and cathedral were built. Augustine thus became the first Archbishop of Canterbury. The town's new importance led to its revival, and trades developed in pottery, textiles, and leather. By 630, gold coins were being struck at the Canterbury mint. In 672, the Synod of Hertford gave the see of Canterbury authority over the entire English Church. In 842 and 851, Canterbury suffered great loss of life during Danish raids.
more...