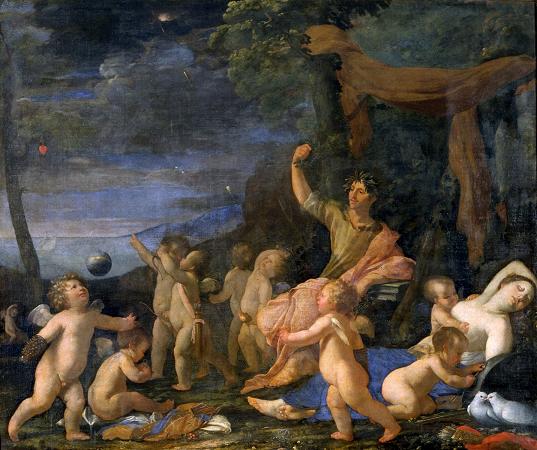
Metamorphoses (8). The Metamorphoses is a Latin narrative poem by the Roman poet Ovid, considered his magnum opus. Comprising 11,995 lines, 15 books and over 250 myths, the poem chronicles the history of the world from its creation to the deification of Julius Caesar within a loose mythico-historical framework. Although meeting the criteria for an epic, the poem defies simple genre classification by its use of varying themes and tones. Ovid took inspiration from the genre of metamorphosis poetry, and some of the Metamorphoses derives from earlier treatment of the same myths; however, he diverged significantly from all of his models. One of the most influential works in Western culture, the Metamorphoses has inspired such authors as Dante Alighieri, Giovanni Boccaccio, Geoffrey Chaucer, and William Shakespeare. Numerous episodes from the poem have been depicted in acclaimed works of sculpture, painting, and music. Although interest in Ovid faded after the Renaissance, there was a resurgence of attention to his work towards the end of the 20th century. Today the Metamorphoses continues to inspire and be retold through various media. The work has been the subject of numerous translations into English, the first by William Caxton in 1480. Ovid's relation to the Hellenistic poets was similar to the attitude of the Hellenistic poets themselves to their predecessors: he demonstrated that he had read their versions. but that he could still treat the myths in his own way., Karl Galinsky Ovid's decision to make myth the dominant subject of the Metamorphoses was influenced by the predisposition of Alexandrian poetry. However, whereas it served in that tradition as the cause for moral reflection or insight, he made it instead the object of play and artful manipulation. The model for a collection of metamorphosis myths derived from a pre-existing genre of metamorphosis poetry in the Hellenistic tradition, of which the earliest known example is Boio Ornithogonia, a now-fragmentary poem collecting myths about the metamorphoses of humans into birds. There are three examples of Metamorphoses by later Hellenistic writers, but little is known of their contents. The Heteroioumena by Nicander of Colophon is better known, and clearly an influence on the poem, 21 of the stories from this work were treated in the Metamorphoses. However, in a way that was typical for writers of the period, Ovid diverged significantly from his models. The Metamorphoses was longer than any previous collection of metamorphosis myths and positioned itself within a historical framework. Some of the Metamorphoses derives from earlier literary and poetic treatment of the same myths. This material was of varying quality and comprehensiveness, while some of it was finely worked, in other cases Ovid may have been working from limited material. In the case of an oft-used myth such as that of Io in Book I, which was the subject of literary adaptation as early as the 5th century BC, and as recently as a generation prior to his own, Ovid reorganises and innovates existing material in order to foreground his favoured topics and to embody the key themes of the Metamorphoses. Scholars have found it difficult to place the Metamorphoses in a genre. The poem has been considered as an epic or a type of epic; a Kollektivgedicht that pulls together a series of examples in miniature form, such as the epyllion; a sampling of one genre after another; or simply a narrative that refuses categorization.
more...