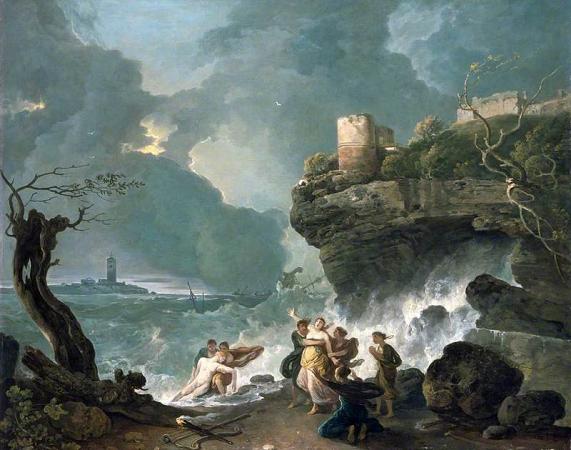
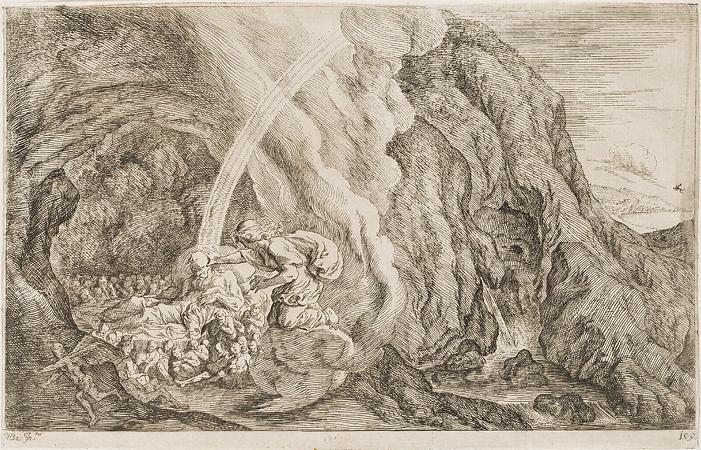
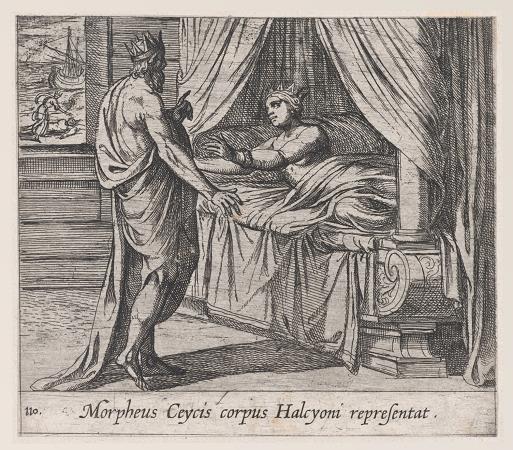
Ceyx. In Greek mythology, Ceyx was the son of Eosphorus and husband of Alcyone, daughter of Aeolus. Ceyx and Alcyone were very happy together, and according to Pseudo-Apollodorus's account, often called each other Zeus and Hera. This angered Zeus, so while Ceyx was at sea, the god threw a thunderbolt at his ship. Ceyx appeared to Alcyone as an apparition to tell her of his fate, and she threw herself into the sea in her grief. Out of compassion, the gods changed them both into halcyon birds. It is said that the halcyon birds build their nests when the water is calm since both of them died at sea. Ovid and Hyginus both also recount the metamorphosis of the pair in and after Ceyx's loss in a storm, though they both omit Ceyx and Alcyone calling each other Zeus and Hera-and Zeus's resulting anger-as a reason for it. They both also make the metamorphosis the origin of the etymology for halcyon days, the seven days in winter when storms never occur. They state that these were originally the seven days each year during which Alcyone laid her eggs and made her nest on the beach and during which her father Aeolus, god of the winds, restrained the winds and calmed the waves so she could do so in safety. The phrase has since come to refer to a peaceful time generally. The myth is also briefly referred to by Virgil, again without reference to Zeus's anger. Various kinds of kingfishers are named after the couple, in reference to the metamorphosis myth: The genus Ceyx is named after him. The kingfisher family Halcyonidae is named after his wife, as is the genus Halcyon. The belted kingfisher's Latin species name also references her name. Their story features in The Book of the Duchess.
more...