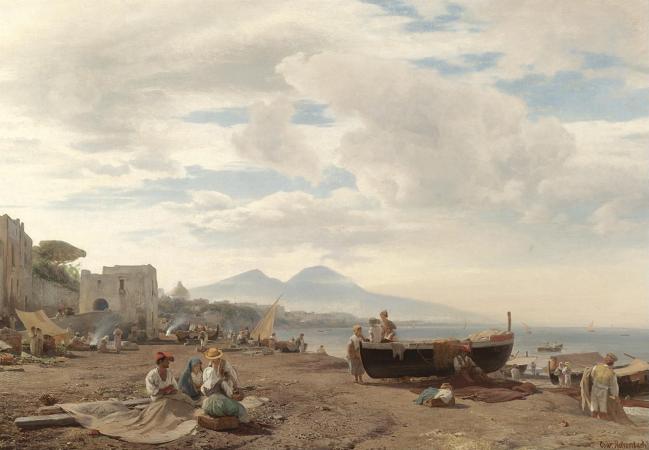
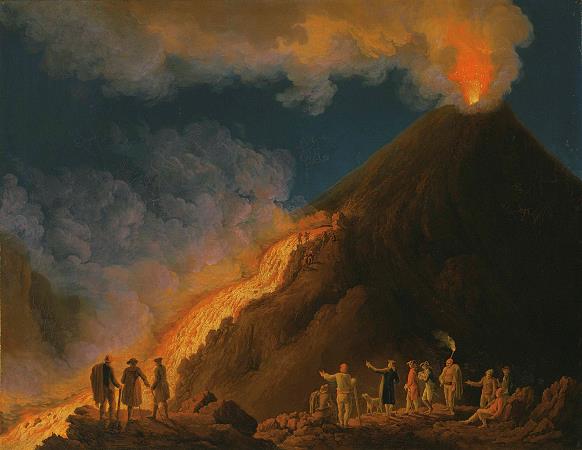
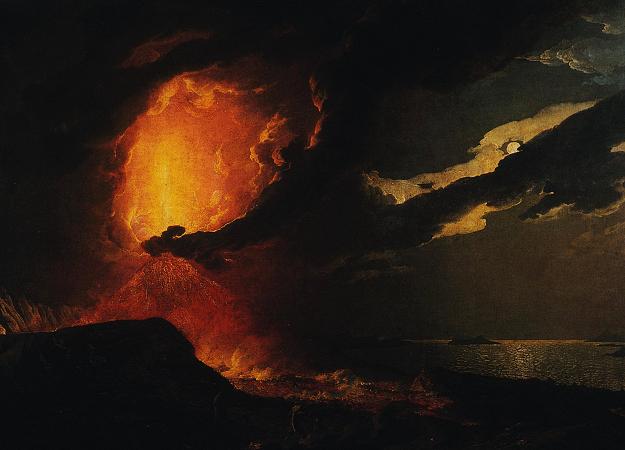
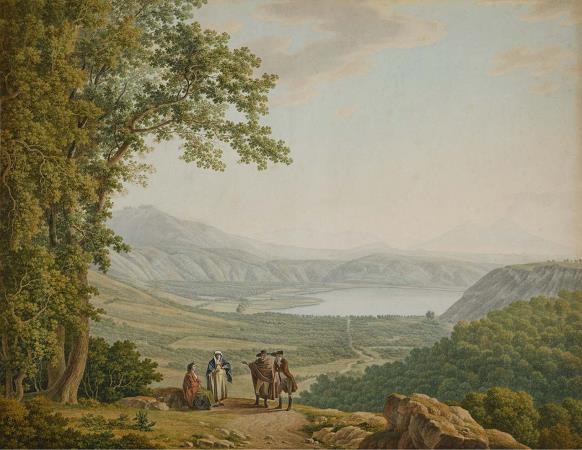
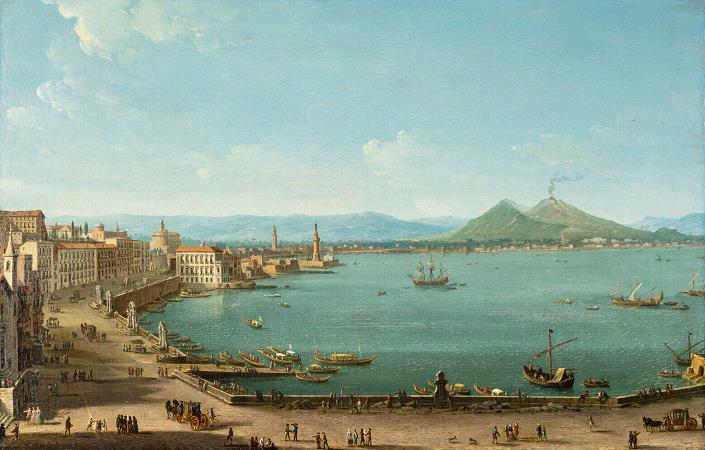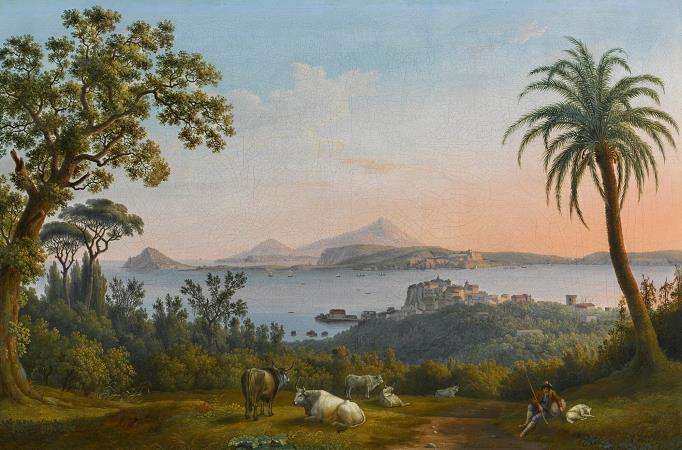Mount Vesuvius. Mount Vesuvius is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about 9 km east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of several volcanoes which form the Campanian volcanic arc. Vesuvius consists of a large cone partially encircled by the steep rim of a summit caldera caused by the collapse of an earlier and originally much higher structure. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79 destroyed the Roman cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum, Oplontis and Stabiae, as well as several other settlements. The eruption ejected a cloud of stones, ashes and volcanic gases to a height of 33 km, erupting molten rock and pulverized pumice at the rate of 610 5 cubic metres per second, ultimately releasing 100,000 times the thermal energy released by the Hiroshima-Nagasaki bombings. More than 1,000 people died in the eruption, but exact numbers are unknown. The only surviving eyewitness account of the event consists of two letters by Pliny the Younger to the historian Tacitus. Vesuvius has erupted many times since and is the only volcano on the European mainland to have erupted within the last hundred years. Today, it is regarded as one of the most dangerous volcanoes in the world because of the population of 3,000,000 people living near enough to be affected, with 600,000 in the danger zone, making it the most densely populated volcanic region in the world, as well as its tendency towards violent, explosive eruptions of the Plinian type. Vesuvius has a long historic and literary tradition. It was considered a divinity of the Genius type at the time of the eruption of AD 79: it appears under the inscribed name Vesuvius as a serpent in the decorative frescos of many lararia, or household shrines, surviving from Pompeii. An inscription from Capua to IOVI VESVVIO indicates that he was worshipped as a power of Jupiter; that is, Jupiter Vesuvius. The Romans regarded Mount Vesuvius to be devoted to Hercules. The historian Diodorus Siculus relates a tradition that Hercules, in the performance of his labors, passed through the country of nearby Cumae on his way to Sicily and found there a place called the Phlegraean Plain, from a hill which anciently vomited out fire. now called Vesuvius. It was inhabited by bandits, the sons of the Earth, who were giants. With the assistance of the gods he pacified the region and went on. The facts behind the tradition, if any, remain unknown, as does whether Herculaneum was named after it. An epigram by the poet Martial in 88 AD suggests that both Venus, patroness of Pompeii, and Hercules were worshipped in the region devastated by the eruption of 79. Vesuvius was a name of the volcano in frequent use by the authors of the late Roman Republic and the early Roman Empire. Its collateral forms were Vesaevus, Vesevus, Vesbius and Vesvius. Writers in ancient Greek used or. Many scholars since then have offered an etymology. As peoples of varying ethnicity and language occupied Campania in the Roman Iron Age, the etymology depends to a large degree on the presumption of what language was spoken there at the time. Naples was settled by Greeks, as the name Nea-polis, New City, testifies. The Oscans, a native Italic people, lived in the countryside. The Latins also competed for the occupation of Campania. Etruscan settlements were in the vicinity. Other peoples of unknown provenance are said to have been there at some time by various ancient authors. Some theories about its origin are: From Greek = not prefixed to a root from or related to the Greek word = I quench, in the sense of unquenchable. From Greek = I hurl and violence, hurling violence, *vesbia, taking advantage of the collateral form. From an Indo-European root, *eus-< *ewes-< *wes-, shine sense the one who lightens, through Latin or. From an Indo-European root *wes = hearth. Vesuvius is a humpbacked peak, consisting of a large cone partially encircled by the steep rim of a summit caldera caused by the collapse of an earlier and originally much higher structure called Mount Somma. The Gran Cono was produced during the A.D. 79 eruption. For this reason, the volcano is also called Somma-Vesuvius or Somma-Vesuvio. The caldera started forming during an eruption around 17,000-18,000 years ago, and was enlarged by later paroxysmal eruptions, ending in the one of AD 79. This structure has given its name to the term somma volcano, which describes any volcano with a summit caldera surrounding a newer cone. The height of the main cone has been constantly changed by eruptions but was 1,281 m in 2010.
more...