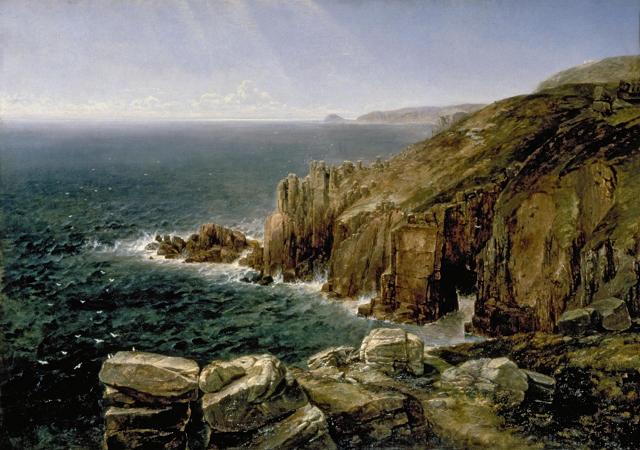
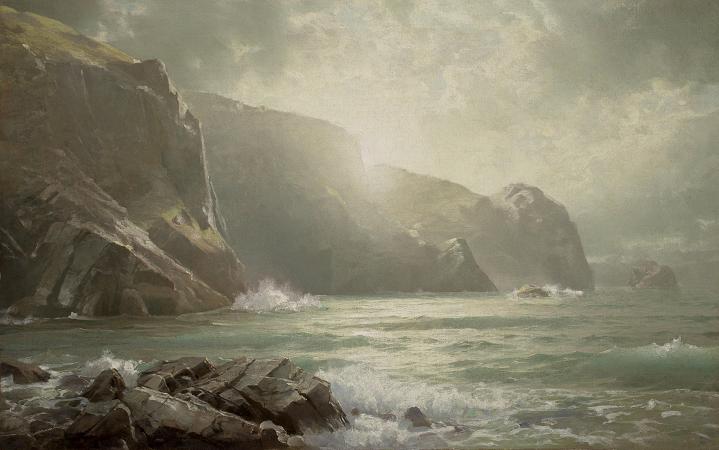
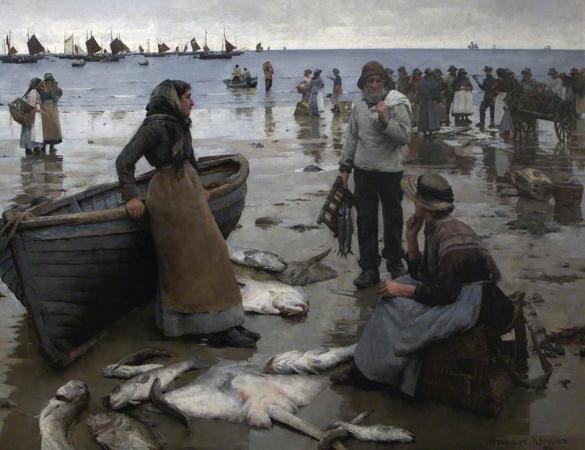
Cornwall. Cornwall is a ceremonial county in South West England, bordered to the north and west by the Celtic Sea, to the south by the English Channel, and to the east by Devon, the River Tamar forming the border between them. Cornwall is the westernmost part of the South West Peninsula of the island of Great Britain. The southwesternmost point is Land's End and the southernmost Lizard Point. Cornwall has a population of 568,210 and an area of 3,563 km 2. The county has been administered since 2009 by the unitary authority, Cornwall Council. The ceremonial county of Cornwall also includes the Isles of Scilly, which are administered separately. The administrative centre of Cornwall is Truro, its only city. Cornwall is the homeland of the Cornish people and the cultural and ethnic origin of the Cornish diaspora. It retains a distinct cultural identity that reflects its history, and is recognised as one of the Celtic nations. It was formerly a Brythonic kingdom and subsequently a royal duchy. The Cornish nationalist movement contests the present constitutional status of Cornwall and seeks greater autonomy within the United Kingdom in the form of a devolved legislative Cornish Assembly with powers similar to those in Wales and Scotland. In 2014, Cornish people were granted minority status under the European Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities, giving them recognition as a distinct ethnic group. Few Roman remains have been found in Cornwall, and there is little evidence that the Romans settled or had much military presence there. After the collapse of the Roman Empire, Cornwall was a part of the Brittonic kingdom of Dumnonia, ruled by chieftains of the Cornovii who may have included figures regarded as semi-historical or legendary, such as King Mark of Cornwall and King Arthur, evidenced by folklore traditions derived from the Historia Regum Britanniae. The Cornovii division of the Dumnonii tribe were separated from their fellow Brythons of Wales after the Battle of Deorham in 577 AD, and often came into conflict with the expanding English kingdom of Wessex. The regions of Dumnonia outside of Cornwall had been annexed by the English by 838 AD. King Athelstan in 936 AD set the boundary between the English and Cornish at the high water mark of the eastern bank of the River Tamar. From the Early Middle Ages, language and culture were shared by Brythons trading across both sides of the Channel, resulting in the corresponding high medieval Breton kingdoms of Domnonee and Cornouaille and the Celtic Christianity common to both areas. Tin mining was important in the Cornish economy from the High Middle Ages, and expanded greatly in the 19th century when rich copper mines were also in production. In the mid-19th century, tin and copper mines entered a period of decline and china clay extraction became more important. Mining had virtually ended by the 1990s. Fishing and agriculture were the other important sectors of the economy, but railways led to a growth of tourism in the 20th century after the decline of the mining and fishing industries. Cornwall is noted for its geology and coastal scenery. A large part of the Cornubian batholith is within Cornwall. The north coast has many cliffs where exposed geological formations are studied. The area is noted for its wild moorland landscapes, its long and varied coastline, its attractive villages, its many place-names derived from the Cornish language, and its very mild climate. Extensive stretches of Cornwall's coastline, and Bodmin Moor, are protected as an Area of Outstanding Natural Beauty. The modern English name Cornwall is a compound of two ancient demonyms coming from two different language groups: Corn-originates from the Brythonic tribe, the Cornovii. The Celtic word kernou is cognate with the English word horn. -wall derives from the Old English exonym walh, meaning foreigner or Roman. In the Cornish language, Cornwall is known as Kernow which stems from a similar linguistic background. The area now known as Cornwall was first inhabited in the Palaeolithic and Mesolithic periods.
more...