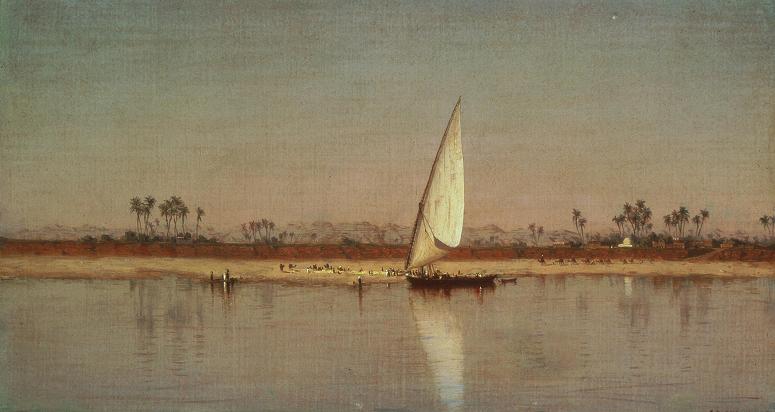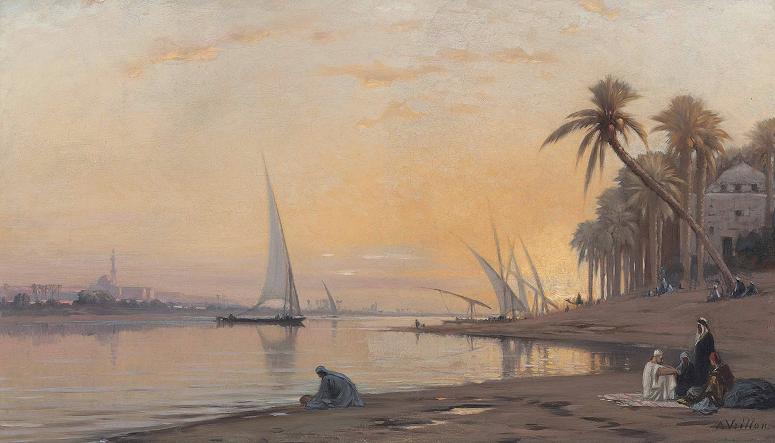Nile River. The Nile is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa, and is the longest river in Africa and the disputed longest river in the world, as the Brazilian government says that the Amazon River is longer than the Nile. The Nile, which is about 6,650 km long, is an international river as its drainage basin covers eleven countries: Tanzania, Uganda, Rwanda, Burundi, the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Kenya, Ethiopia, Eritrea, South Sudan, Republic of the Sudan, and Egypt. In particular, the Nile is the primary water source of Egypt and Sudan. The Nile has two major tributaries, the White Nile and the Blue Nile. The White Nile is considered to be the headwaters and primary stream of the Nile itself. The Blue Nile, however, is the source of most of the water and silt. The White Nile is longer and rises in the Great Lakes region of central Africa, with the most distant source still undetermined but located in either Rwanda or Burundi. It flows north through Tanzania, Lake Victoria, Uganda and South Sudan. The Blue Nile begins at Lake Tana in Ethiopia and flows into Sudan from the southeast. The two rivers meet just north of the Sudanese capital of Khartoum. The northern section of the river flows north almost entirely through the Sudanese desert to Egypt, then ends in a large delta and flows into the Mediterranean Sea. Egyptian civilization and Sudanese kingdoms have depended on the river since ancient times. Most of the population and cities of Egypt lie along those parts of the Nile valley north of Aswan, and nearly all the cultural and historical sites of Ancient Egypt are found along river banks. The standard English names White Nile and Blue Nile, to refer to the river's source, derive from Arabic names formerly applied only to the Sudanese stretches which meet at Khartoum. Beyond that, however, the etymology is disputed. Hesiod at his Theogony refers that Nilus was one of the Potamoi, son of Oceanus and Tethys. Another derivation of Nile might be related to the term Nil, which refers to Indigofera tinctoria, one of the original sources of indigo dye; or Nymphaea caerulea, known as The Sacred Blue Lily of the Nile, which was found scattered over Tutankhamen's corpse when it was located in 1922. Another possible etymology derives it from a Semitic Nahar, meaning river. With a total length of about 6,650 km between the region of Lake Victoria and the Mediterranean Sea, the Nile is the longest river on the African continent. The drainage basin of the Nile covers 3,254,555 square kilometers, about 10% of the area of Africa. Compared to other major rivers, though, the Nile carries little water. The Nile basin is complex, and because of this, the discharge at any given point along the mainstem depends on many factors including weather, diversions, evaporation and evapotranspiration, and groundwater flow. Above Khartoum, the Nile is also known as the White Nile, a term also used in a limited sense to describe the section between Lake No and Khartoum. At Khartoum the river is joined by the Blue Nile. The White Nile starts in equatorial East Africa, and the Blue Nile begins in Ethiopia. Both branches are on the western flanks of the East African Rift. The source of the Nile is sometimes considered to be Lake Victoria, but the lake has feeder rivers of considerable size. The Kagera River, which flows into Lake Victoria near the Tanzanian town of Bukoba, is the longest feeder, although sources do not agree on which is the longest tributary of the Kagera and hence the most distant source of the Nile itself.
more...