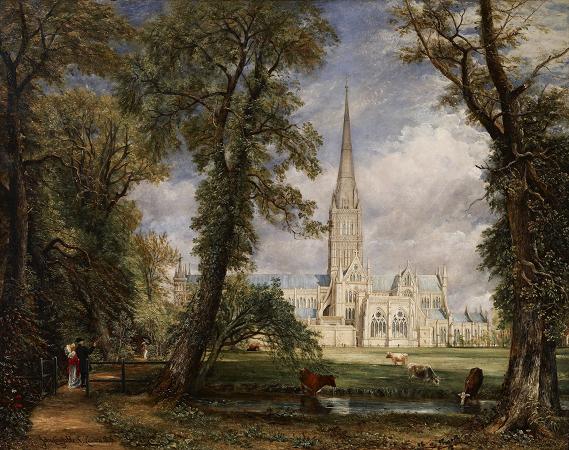
Landscape with Church. A church, church building or church house is a building used for Christian worship services and other Christian religious activities. The earliest identified Christian church is a house church founded between 233 and 256. From the 11th through the 14th centuries, there was a wave of church construction in Western Europe. Sometimes, the word church is used by analogy for the buildings of other religions. Church is also used to describe the Christian religious community as a whole, or a body or an assembly of Christian believers around the world. In traditional Christian architecture, the plan view of a church often forms a Christian cross; the center aisle and seating representing the vertical beam with the bema and altar forming the horizontal. Towers or domes may inspire contemplation of the heavens. Modern churches have a variety of architectural styles and layouts. Some buildings designed for other purposes have been converted to churches, while many original church buildings have been put to other uses. The word church is derived from Old English, place of assemblage set aside for Christian worship, from the Proto-Germanic kirika. This was probably borrowed via the Gothic from the Greek, the Lord's, from, ruler, lord. in turn comes from the Proto-Indo-European language root meaning to swell. The Greek, of the Lord, was used of houses of Christian worship, especially in the East, although it was less common in this sense. The earliest archeologically identified Christian church is a house church, the Dura-Europos church, founded between 233 and 256. In the second half of the 3rd century AD, the first purpose-built halls for Christian worship began to be constructed. Although many of these were destroyed early in the next century during the Diocletianic Persecution. Even larger and more elaborate churches began to appear during the reign of the Emperor Constantine the Great. From the 11th through the 14th centuries, a wave of cathedral-building and construction of smaller parish churches occurred across Western Europe. Besides serving as a place of worship, the cathedral or parish church was frequently employed as a general gathering-place by the communities in which they were located, hosting such events as guild meetings, banquets, mystery plays, and fairs. Church grounds and buildings were also used for the threshing and storage of grain. Between 1000 and 1200 the romanesque style became popular across Europe. The romanesque style is defined by large and bulky edifices that are typically made up of simple, compact, sparsely decorated geometric structures. Frequent features of the Romanesque church include circular arches, round or octagonal towers and cushion capitals on pillars. In the early romanesque era, coffering on the ceiling was fashionable, while later in the same era, groined vault gained popularity. Interiors widened and the motifs of sculptures took on more epic traits and themes. The Gothic style emerged around 1140 in Ile-de-France and subsequently spread throughout Europe. Gothic churches lost the compact qualities of the romanesque era and decorations often contained symbolic and allegorical features. The first pointed arches, rib vaults and buttresses began to appear, all possessing geometric properties that reduced the need for large, rigid walls to ensure structural stability. This also permitted the size of windows to increase, producing brighter and lighter interiors. Nave ceilings became higher and pillars and steeples grew taller. Many architects used these developments to push the limits of structural possibility, an inclination which resulted in the collapse of several towers possessing designs that had unwittingly exceeded the boundaries of soundness. In Germany, the Netherlands, and Spain, it became popular to build hall churches, a style in which every vault would be built to the same height. Gothic cathedrals were lavishly designed, as in the romanesque era, and many share romanesque traits. However, several also exhibit unprecedented degrees of detail and complexity in decoration. The Notre-Dame de Paris and Notre-Dame de Reims in France, as well as the San Francesco d'Assisi in Palermo, and the Salisbury Cathedral and Wool Church in England and Santhome Church in Chennai, India shows the elaborate stylings characteristic of Gothic cathedrals. Some of the most well-known gothic churches remained unfinished for centuries, after the gothic style fell out of popularity.
more...