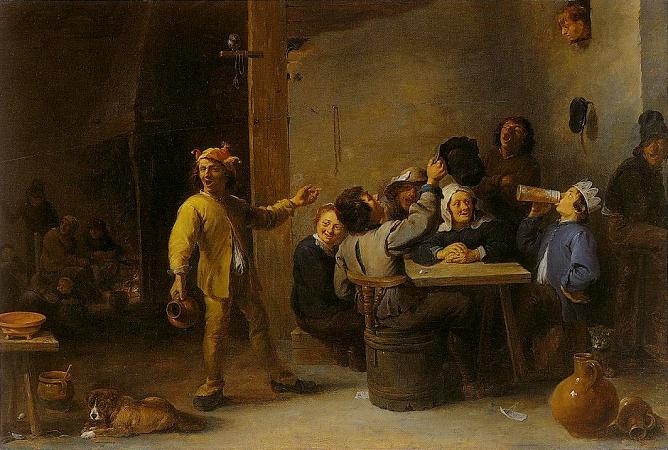
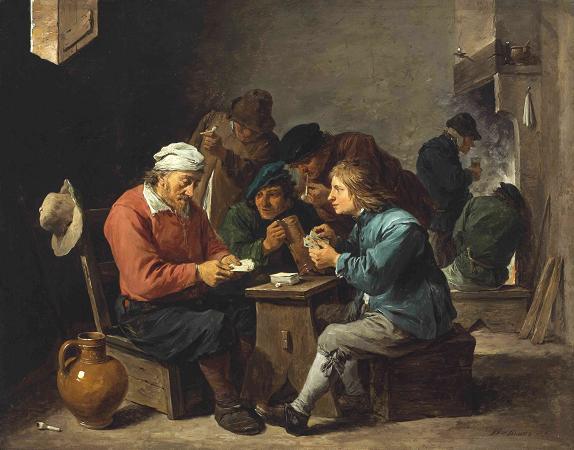
David Teniers the Younger (1610 - 1690). David Teniers the Younger or David Teniers II was a Flemish Baroque painter, printmaker, draughtsman, miniaturist painter, staffage painter, copyist and art curator. He was an extremely versatile artist known for his prolific output. He was an innovator in a wide range of genres such as history painting, genre painting, landscape painting, portrait and still life. He is now best remembered as the leading Flemish genre painter of his day. Teniers is particularly known for developing the peasant genre, the tavern scene, pictures of collections and scenes with alchemists and physicians. He was court painter and the curator of the collection of Archduke Leopold Wilhelm, the art loving Governor General of the Habsburg Netherlands. He created a printed catalogue of the collections of the Archduke. He was the founder of the Antwerp Academy, where young artists were trained to draw and sculpt in the hope of reviving Flemish art after its decline following the death of the leading Flemish artists Rubens and Anthony van Dyck in the early 1640s. He influenced the next generation of Northern genre painters as well as French Rococo painters such as Antoine Watteau. David Teniers the Younger was born in Antwerp as the son of David Teniers the Elder and Dymphna de Wilde. His father was a painter of altarpieces and small-scale cabinet paintings. Three of his brothers also became painters: Juliaan III, Theodoor and Abraham. The work of his two oldest brothers is virtually unknown. The work of his youngest brother Abraham was very close to David's own. From 1626 David the younger studied under his father. A collaborator of his father early on in his career, the father and son pair created together a series of twelve panels recounting stories from Torquato Tasso's epic Gerusalemme Liberata. His father was frequently in financial straits and his debts landed him occasionally in jail. David the younger had to make copies of old masters in order to support the family. In 1632-33 he was registered as 'wijnmeester' in the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke. A David Teniers is recorded in the Antwerp records as having been issued in 1635 a passport to visit Paris. The artist likely also travelled to England as on 29 December 1635 of the same year he signed in Dover a contract with the Antwerp art dealer Chrisostomos van Immerseel, then resident in England. Rubens received in 1636 a commission from the Spanish king Philip IV of Spain to create a series of mythological paintings to decorate the Torre de la Parada, a hunting lodge of the king near Madrid. The mythological scenes depicted in the series were largely based on the Metamorphoses of Ovid. Rubens realized this important commission with the assistance of a large number of Antwerp painters such as Jacob Jordaens, Cornelis de Vos, Jan Cossiers, Peter Snayers, Thomas Willeboirts Bosschaert, Theodoor van Thulden, Jan Boeckhorst, Peeter Symons, Jacob Peter Gowy and others, who worked after Rubens' modellos. Teniers was also invited to participate in this project and make a picture after Rubens' design. That painting is considered lost. Teniers married into the famous Brueghel artist family when Anna Brueghel, daughter of Jan Brueghel the Elder, became his wife on 22 July 1637. Rubens, who had been the guardian of Anna Brueghel after her father's death, was a witness at the wedding. Through his marriage Teniers was able to cement a close relationship with Rubens who had been a good friend and frequent collaborator with his wife's father. This is borne out by the fact that at the baptism of the first of the couple's seven children David Teniers III, Rubens' second wife, Helene Fourment was the godmother. Around this time Teniers started to gain a reputation as an artist and he received many commissions. The Guild of St George, a local militia in Antwerp, commissioned a group portrait in 1643. Teniers was a dean of the Antwerp Guild of Saint Luke in 1644-1645. When Archduke Leopold Wilhelm of Austria became the Governor General of the Southern Netherlands in 1647, the Archduke soon became an important patron of Teniers. The success went to the artist's head. He claimed that his grandfather Julian Taisnier, who had moved from Ath to Antwerp in the 16th century had been from a family that had been entitled to bear a coat of arms. Teniers started to use this coat of arms consisting of a croaching bear on a field of gold encircled by three green acorns. His brother-in-law Jan Baptist Borrekens reported him and Teniers was prohibited from using the coat of arms.
more...