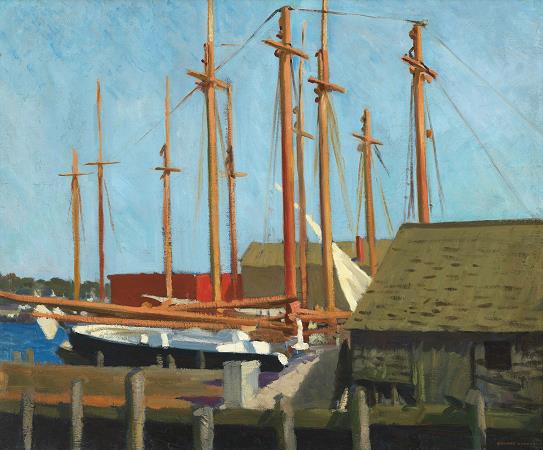
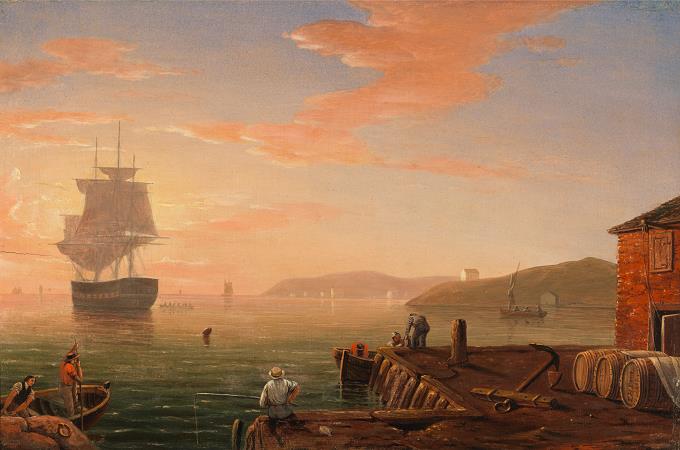
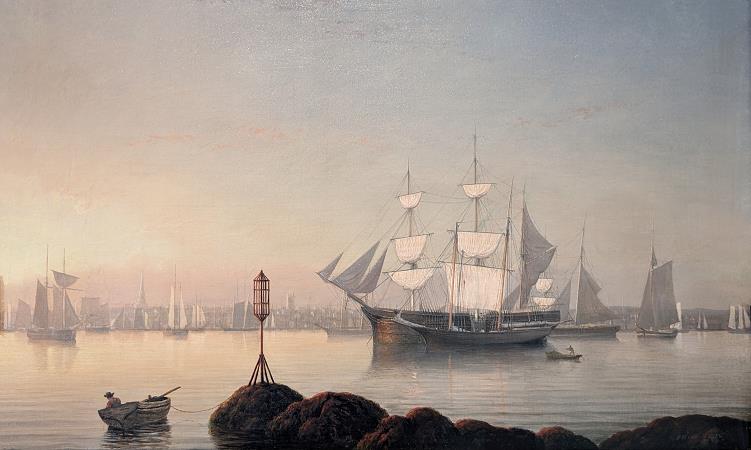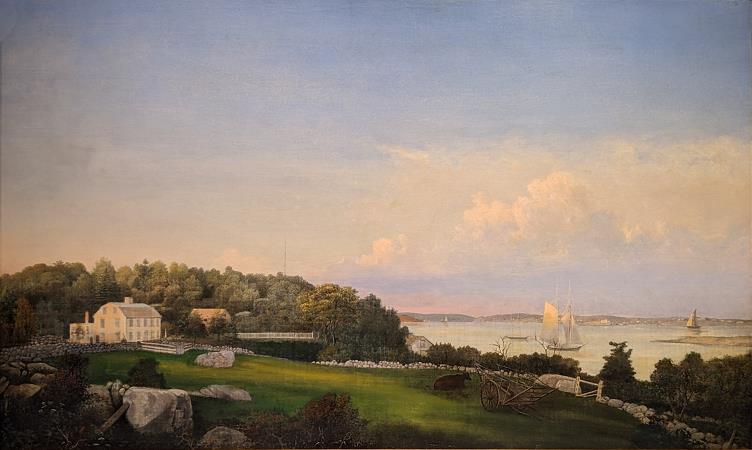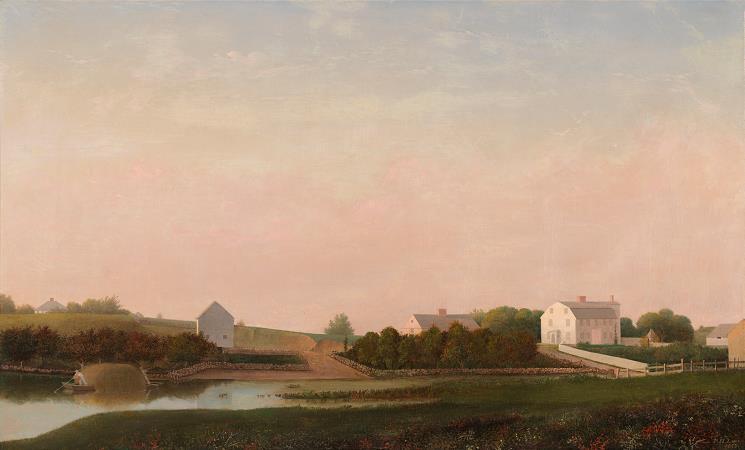Gloucester. Gloucester is a city on Cape Ann in Essex County, Massachusetts, in the United States. It is part of Massachusetts's North Shore. The population was 28,789 at the 2010 U.S. Census. An important center of the fishing industry and a popular summer destination, Gloucester consists of an urban core on the north side of the harbor and the outlying neighborhoods of Annisquam, Bay View, Lanesville, Folly Cove, Magnolia, Riverdale, East Gloucester, and West Gloucester. The boundaries of Gloucester originally included the town of Rockport, in an area dubbed Sandy Bay. That village separated formally on February 27, 1840. In 1873, Gloucester was reincorporated as a city. Gloucester was founded at Cape Ann by an expedition called the Dorchester Company of men from Dorchester chartered by James I in 1623. It was one of the first English settlements in what would become the Massachusetts Bay Colony, and predates both Salem in 1626 and Boston in 1630. The first company of pioneers made landing at Half Moon Beach and settled nearby, setting up fishing stages in a field in what is now Stage Fort Park. This settlement's existence is proclaimed today by a memorial tablet, affixed to a 50-foot boulder in that park. Life in this first settlement was harsh and it was short-lived. Around 1626 the place was abandoned, and the people removed themselves to Naumkeag, where more fertile soil for planting was to be found. The meetinghouse was even disassembled and relocated to the new place of settlement. At some point in the following years-though no record exists-the area was slowly resettled. The town was formally incorporated in 1642. It is at this time that the name Gloucester first appears on tax rolls, although in various spellings. The town took its name from the city of Gloucester in South-West England, perhaps from where many of its new occupants originated but more likely because Gloucester, England, was a Parliamentarian stronghold, successfully defended with the aid of the Earl of Essex against the King in the Siege of Gloucester of 1643. This new permanent settlement focused on the Town Green area, an inlet in the marshes at a bend in the Annisquam River. This area is now the site of Grant Circle, a large traffic rotary at which Massachusetts Route 128 mingles with a major city street. Here the first permanent settlers built a meeting house and therefore focused the nexus of their settlement on the Island for nearly 100 years. Unlike other early coastal towns in New England, development in Gloucester was not focused around the harbor as it is today, rather it was inland that people settled first. This is evidenced by the placement of the Town Green nearly two miles from the harbor-front. The Town Green is also where the settlers built the first school. By Massachusetts Bay Colony Law, any town boasting 100 families or more had to provide a public schoolhouse. This requirement was met in 1698, with Thomas Riggs standing as the town's first schoolmaster. The White-Ellery House was erected in 1710 upon the Town Green. It was built at the edge of a marsh for Gloucester's first settled minister, the Reverend John White. Early industry included subsistence farming and logging. Because of the poor soil and rocky hills, Cape Ann was not well suited for farming on a large scale. Small family farms and livestock provided the bulk of the sustenance to the population. Fishing, for which the town is known today, was limited to close-to-shore, with families subsisting on small catches as opposed to the great bounties yielded in later years. The fisherman of Gloucester did not command the Grand Banks until the mid-18th century. Historian Christine Heyrman, examining the town's society between 1690 and 1750, finds that at the beginning community sensibility was weak in a town that was a loose agglomeration of individuals. Commerce and capitalism transformed the society, making it much more closely knit with extended families interlocking in business relationships. Early Gloucestermen cleared great swaths of the forest of Cape Ann for farm and pasture land, using the timber to build structures as far away as Boston. The rocky moors of Gloucester remained clear for two centuries until the forest reclaimed the land in the 20th century. The inland part of the island became known as the Commons, the Common Village, or Dogtown. Here small dwellings lay scattered amongst the boulders and swamps, along roads that meandered through the hills. These dwellings were at times little more than shanties; only one was even two stories tall. Despite their size, several generations of families were raised in such houses.
more...